So what is the actual situation?
1. The life of an electrolytic capacitor depends on the ambient temperature at which it operates.
How is the life of an electrolytic capacitor defined? Of course it is defined in hours. However, if the life index of an electrolytic capacitor is 1,000 hours, it does not mean that the electrolytic capacitor will be broken after a thousand hours. No, it just means that the capacity of this electrolytic capacitor is reduced by half after 1000 hours. Originally, the capacity was reduced by half. It is 20uF, and now it is only 10uF.
In addition, there is another characteristic of the life index of the electrolytic capacitor, which is to indicate the life in the case of how many degrees of working temperature. And usually it is specified as the life at 105 ° C ambient temperature.
This is because the electrolytic capacitors we use today are electrolytic capacitors using liquid electrolyte. If the electrolyte is dry, the capacitance is of course gone. The higher the temperature, the easier the electrolyte will evaporate. Therefore, the life indicator of the electrolytic capacitor must indicate the life at what ambient temperature.
So all current electrolytic capacitors are marked with a lifetime at 105 °C. For example, the most common electrolytic capacitor has a life of only 1,000 hours at 105 °C. But if you think that all electrolytic capacitors have a life of only 1,000 hours. That's a big mistake.
Simply put, if the ambient temperature is higher than 105 ° C, its life will be less than 1,000 hours, if the ambient temperature is lower than 105 ° C, then its life is higher than 1,000 hours. So is there a rough quantitative relationship between life and temperature? some!
One of the simplest and easy to calculate relationships is that for every 10 degrees increase in ambient temperature, life is reduced by half; in turn, for every 10 degrees decrease in ambient temperature, life expectancy is doubled. Of course this is just a simple estimate, but it is also quite accurate.
Because the electrolytic capacitor used for the LED driving power supply is definitely placed inside the LED lamp housing, we only need to know the internal temperature of the LED lamp to know the working life of the electrolytic capacitor.
2. What is the ambient temperature in the LED fixture?
Because LEDs and electrolytic capacitors are placed in the same housing in many fixtures, the ambient temperature is simply the same. This ambient temperature is mainly determined by the balance of heat and heat dissipation between the LED and the power supply. And the heat and heat dissipation of each LED luminaire is different, so how can we know the ambient temperature?
In fact, this problem can be reversed, that is, a well-designed LED luminaire, which allows the internal ambient temperature to be constant. This is because the junction temperature of the LED chip is the main reason for determining the light decay (life) of the LED chip. The LED junction temperature is of course related to its ambient temperature, so as long as the allowed LED junction temperature is known, it can be inferred from the inside of the LED fixture. Ambient temperature.
However, there are at least three thermal resistances, that is, the thermal resistance θjc of the LED chip to the outer casing, and the thermal resistance of the LED casing to the surface of the aluminum substrate. In fact, it passes through the solder, the copper foil, and the insulating layer to the aluminum plate, but among them The most important is the thermal resistance of the insulating layer, collectively referred to as θlv, and the third is the thermal resistance θla of the air from the aluminum plate to the blister.
Take the 3014 LED, its thermal resistance θjc is 90 ° C / W, because its power is only 0.1W, so the internal and external temperature difference is 9 ° C. The thermal resistance of the aluminum substrate is 1 ° C / W. For a 10 W luminaire, since all 10 W LEDs are mounted on the same aluminum substrate, the total temperature difference is 10 ° C, a total temperature difference of 19 ° C, the last Θla is difficult to estimate because it is related to the circulation of air. In the case where the internal air does not flow, the temperature difference is only about 1 °C, so the total is 20 °C. That is, the LED junction temperature is equal to the ambient temperature plus 20 °C.
So can the ambient temperature inside the bulb allow 105 degrees? Just look at the picture below and you will know. That is the relationship between Cree's LED chip junction temperature and light decay.
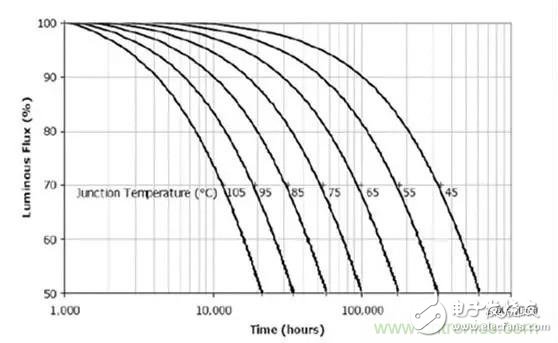
If the ambient temperature is 105 ° C, then at least 20 ° C is the junction temperature, so the junction temperature is about 125 ° C. It has not been found on this curve and can only be roughly estimated to have a lifetime of only 4,000 hours. This is absolutely unacceptable! In other words, the ambient temperature in the LED bulb must be much lower than 105 °C!
We can in turn see what the ambient temperature should be based on the required LED lifetime. Suppose we require the LED to have a lifetime of 100,000 hours, then its junction temperature can only be lower than 65 ° C, so the ambient temperature must be lower than 45 ° C. That is, the working temperature of the electrolytic capacitor must be lower than 45 ° C .
3, the actual life of electrolytic capacitors of various lifespan at an ambient temperature of 45 ° C
Now that we know the working environment temperature of the electrolytic capacitor in the actual LED luminaire, it is easy to calculate its actual life. We list the actual lifetimes of several commonly used electrolytic capacitors in the table below.
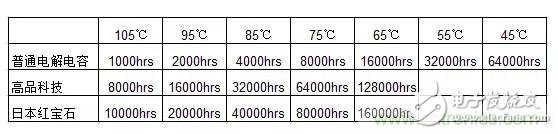
As can be seen from the table, even the most common 1,000-hour electrolytic capacitor can reach 64,000 hours at an ambient temperature of 45 ° C. For ordinary LED lamps nominally 50,000 hours is already Enough.
4, the method of extending the life of electrolytic capacitors
4.1 extending its life from design
In fact, to extend the life of the electrolytic capacitor, the method is very simple, because its end of life is mainly due to the evaporation of the liquid electrolyte, if it improves its sealing, does not let it evaporate, its life is naturally extended. For example, EvoxRifa's two-layer sealing system slows down the evaporation rate of the electrolyte.
Also, the loss of electrolyte can be greatly reduced by using a phenolic plastic cover with an electrode wound integrally and a double special gasket to be tightly engaged with the aluminum casing.
4.2 Extend its life from use
Reducing the ripple current can also extend its service life. If the ripple current is too large, it can be reduced by connecting two capacitors in parallel.
4.3 Select to extend its life
In the selection of electrolytic capacitors, in addition to the selection of brand-name electrolytic capacitors to ensure quality, there is still a margin in terms of voltage and capacity. For example, for 220V after bridge rectification, its DC voltage will be as high as 300V, but at least 450V withstand voltage electrolytic capacitor is used when selecting electrolytic capacitor. If you need 10uF for calculation, it is best to use 20uF. These measures can also extend the life of electrolytic capacitors. Since the internal resistance of the capacitor is higher than the ambient temperature due to the equivalent resistance and ripple current of the capacitor, it is necessary to leave room for it.
5, protect the electrolytic capacitor
Sometimes even if a long-life electrolytic capacitor is used, it is often found that the electrolytic capacitor is broken. What is the reason?
In fact, if you think that this is the quality of electrolytic capacitors, it is really a matter of letting the electrolytic capacitors suffer! In fact, at this time, the electrolytic capacitor is not the perpetrator, but the victim. Why do you say this way?
Because we know that in the AC power grid of the city, there are often high-voltage surges due to lightning strikes. Although many lightning protection measures have been made for lightning strikes on the large power grid, it is still inevitable that the fish leaking out to the residents will be inevitable. Home.
The US power grid should be very advanced, but one thing happened in my house. After a lightning strike, I found that my fax machine could not work. After careful inspection, it was because the lightning was destroyed and the power was completely destroyed. It can only be scrapped.
If the LED luminaire is powered by the mains, then the anti-surge measures must be added to the mains input of the luminaire, including fuses, and overvoltage protection resistors, commonly referred to as varistors. Protect the components behind, otherwise the long-lived electrolytic capacitor will be broken down by the surge voltage.
I believe that if all LED manufacturers can use regular high-quality electrolytic capacitors and adopt the above-mentioned measures, then the electrolytic capacitors will be cleaned!
SFP standardization:
SFP transceivers are regulated by a multilateral agreement (MSA) between competing manufacturers. SFP is designed according to GBIC interface, allowing a greater port density (the number of transceivers per inch on the side of the motherboard) than GBIC, so SFP is also called "mini-GBIC". The related small package transceiver (SFF transceiver) is smaller in size than SFP, but SFF is soldered to the motherboard as a pin through-hole device instead of being inserted into the side card slot on.
SFP transceivers have a variety of different transmission and reception types. Users can select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the "optical performance" that can be achieved based on the available fiber types (such as multimode fiber or single mode fiber). Available optical SFP modules are generally divided into the following categories: 850nm wavelength/550m distance MMF (SX), 1310nm wavelength/10km distance SMF (LX), 1550nm wavelength/40km distance XD, 80km distance ZX, EX or EZX with a distance of 120 kilometers, and DWDM. The SFP transceiver also provides a copper cable interface, so that host devices designed mainly for optical fiber communication can also communicate through UTP network cables. There are also wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) and single-fiber "bidirectional" (1310/1490nm wavelength upstream/downstream) SFP.
Commercial SFP transceivers can provide rates up to 4.25 G bps. Several packaging forms of 10 Gbps transceivers are XFP, and a new variant "SFP+" which is basically the same as the SFP package.
Epon Sfp Module,Gpon Sfp Module,Px20++ Sfp,C++ Sfp
Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com