
LED is called the most promising green lighting source in the 21st century because of its high brightness, low heat, long life, non-toxic, recyclable and other advantages. Statistics show that if 50% of China's light source is replaced by LED, it will achieve an annual power saving of 210 billion kWh, equivalent to the construction of 2.5 Three Gorges Project. At the same time, it has incomparable advantages in terms of life and application flexibility, and will become the inevitable development direction of future lighting.
The principle of LED illumination is to directly convert electrical energy into light energy. The electro-optical conversion efficiency is about 20%-30%, and the photothermal conversion efficiency is about 70%-80%. As the chip size decreases and the power is greatly increased, the LED junction temperature remains high, causing a series of problems such as reduced light intensity, spectral shift, color temperature rise, thermal stress increase, and accelerated aging of components. Greatly reduce the life of the LED. Junction temperature is also an important technical indicator to measure the thermal performance of LED packages . When the junction temperature rises above the maximum allowable temperature (150 ° C), high-power LEDs will be damaged by overheating. Therefore, in high-power LED packaging equipment, heat dissipation is a bottleneck that limits its development and is a key issue that must be solved.
At present, the global LED industry solves the problem of heat dissipation by three aspects. One is the package structure, the other is the package material, and the heat sink substrate. Only by dissipating heat can the fundamental problem be solved.
There are three main types of package structures currently used for heat dissipation:
First, flip chip structure
In the traditional dressing chip, the electrode is located on the light-emitting surface of the chip, so that part of the light is blocked and the light-emitting efficiency of the chip is lowered. At the same time, the heat generated by the PN junction of this structure is derived through the sapphire substrate. The sapphire has a low thermal conductivity and a long heat transfer path, so that the chip has a large thermal resistance and heat is not easily emitted. From the optical point of view and thermal point of view, this structure has some shortcomings. In order to overcome the shortage of the pre-loaded chip, in 2001 Lumileds Lighting developed a flip-chip structure chip. The chip of the structure, the light is taken out from the top sapphire, the shading of the electrode and the lead wire is eliminated, the light-emitting efficiency is improved, and the ceramic circuit board with high thermal conductivity is used for the substrate, which greatly improves the heat dissipation effect of the chip.
Second, the micro-spray structure
In the package system, the fluid in the fluid chamber forms a strong jet at a series of micro-jets under a certain pressure, and the jet directly impacts the lower surface of the LED chip substrate and carries away the heat generated by the LED chip in the micropump. Under the action, the heated fluid enters the small fluid cavity to release heat to the external environment, so that its temperature drops, and flows into the micro pump again to start a new cycle. Similar to the water-cooling heat dissipation of the computer motherboard, the micro-spray structure has the advantages of high heat dissipation efficiency and uniform temperature distribution of the LED chip substrate, but the reliability and stability of the micro-pump have a great influence on the system, and the system structure is complicated. Higher operating costs.
Third, thermoelectric refrigeration structure
A thermoelectric cooler is a semiconductor device whose PN junction is composed of two different conductive materials, one carrying a positive charge and the other carrying a negative charge. When a current passes through a junction, the two charges leave the junction region and simultaneously There is heat to achieve the purpose of refrigeration. Similar to the principle of air conditioning refrigeration. But the technology is not mature enough to be applied in batches.
It can be seen from the above that the overall heat dissipation effect of the LED has a great relationship with the heat dissipation between the interfaces, so that the thermal resistance of an interface can be completely reduced to improve the heat dissipation effect. Packaging materials are one of them. The packaging material is mainly the substrate and glue. At present, LED package glue commonly used are thermal conductive glue, conductive silver glue and the latest fluorescent ceramic glue.
First, thermal adhesive
The main component of the commonly used thermal adhesive is epoxy resin, so its thermal conductivity is small, thermal conductivity is poor, and thermal resistance is large. In order to improve its thermal conductivity, a high thermal conductivity material such as aluminum oxide, boron nitride, silicon carbide or the like is usually filled inside the substrate. The thermal conductive adhesive has the advantages of insulation, heat conduction, shockproof, convenient installation, simple process, etc., but its thermal conductivity is very low (generally lower than 1w/mk), so it can only be applied to LED packaging devices that do not require high heat dissipation. If the LED power is too large, the thermal conductivity will not keep up with the demand, and a large amount of junction temperature will also be generated.
Second, conductive silver glue
The conductive silver paste is a GeAs, SiC conductive substrate LED, a red, yellow, yellow-green chip LED package with a back electrode, or a key packaging material in the glue preparation process, having a fixed bonding chip, conductive and heat conduction, and transmission. The role of heat has an important influence on the heat dissipation, light reflectivity, VF characteristics, and the like of the LED device. But the technology is not very mature, the cost is high, and it is not popular.
Fourth, fluorescent ceramic glue
It has the best optical quality, highest performance, high hardness, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. It belongs to the new technology and is much better than the traditional conductive adhesive, but it is still in the experimental stage and has not been formed.
Through the above analysis, it can be seen that the real heat-dissipating interface materials are still under development, and the application still takes a certain period of time. A certain heat dissipation method of the LED package device is from the LED chip to the bonding layer to the internal heat sink to the heat sink substrate and finally to the external environment. It can be seen that the heat dissipation substrate is important for the heat dissipation of the LED package, and therefore the heat dissipation substrate must have the following characteristics: high Thermal conductivity, insulation, stability, flatness and high strength.
First, the metal substrate
The metal substrate is bonded to the metal with high thermal conductivity (copper, aluminum, etc.) on the original printed circuit board to improve the heat dissipation effect of the electronic device. It is a key link connecting the internal and external heat dissipation paths. The advantage of the metal substrate is that it is relatively low in cost and can be mass-produced, but it also has certain disadvantages: 1 The thermal conductivity is low, and the thermal conductivity of the MCPCB can reach 1-2.2 W/(m· K). 2 The thickness of the insulating layer in the metal substrate structure should be moderate, neither too thick nor too thin. The insulation layer is too thick to increase the thermal resistance of the entire metal substrate to affect the heat dissipation effect; the insulation layer is too thin, and if the voltage applied to the metal substrate is too high, the insulation layer may be broken, resulting in a short circuit.
Second, the ceramic substrate
The ceramic sintered substrate has good heat dissipation, high temperature resistance, moisture resistance, breakdown voltage, and breakdown voltage, and has good thermal expansion coefficient matching, and has the characteristics of reducing thermal stress and thermal deformation. Therefore, the ceramic substrate becomes an important substrate material in a high-power LED package. At present, the most commonly used ceramic materials are alumina, aluminum nitride, cerium oxide, silicon carbide, and the like.
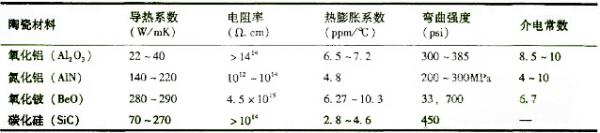
in conclusion:
1) In high-power LED package devices, to achieve low thermal resistance and fast heat dissipation, packaging materials have become a key technology. It is a hot topic in the future to find more excellent packaging materials to improve the heat dissipation of LED package devices.
2) To solve the heat dissipation problem of high-power LED package devices, it is necessary to select suitable packaging materials (including thermal interface materials and substrate materials, etc.). In the process of selecting the thermal interface material and the substrate material, the appropriate material should be selected according to the appropriate occasion. The common thermal interface material used in general high-power LED packages is conductive silver paste, and the more common substrate used is ceramic circuit board.
Capillary Pressure Gauge,2 In 1 Bi-Metal Thermomanometer,Pump Pressure Gauge,Copper Pipe Manometer
ZHOUSHAN JIAERLING METER CO.,LTD , https://www.zsjrlmeter.com