The computer network topology refers to the form in which each site in the network is connected to each other. In the local area network, it is clear that it is the connection form of file servers, workstations, and cables. The main current topologies are bus topology, star topology, ring topology, tree topology (evolved from bus type) and their hybrid types. As the name implies, the bus type actually connects the file server and the workstation to a common cable called a bus, and the bus must have terminators at both ends. The star topology uses a device as the central connection point. Each station has a It is directly connected to form a star; and the ring topology is to connect all stations to each other in series, forming a loop like a chain. Mixing these three basic topologies together is naturally a hybrid!
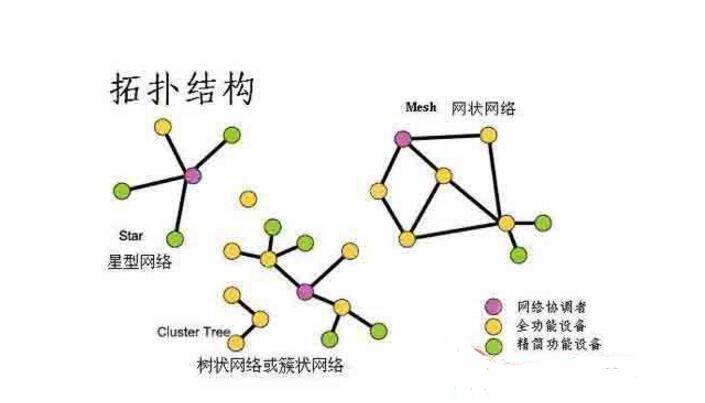
The topological structure of computer networks is a method of referring to the relationship between dots and lines that are not related to size and shape in topology. The computer and communication equipment in the network is abstracted as a point, the transmission medium is abstracted into a line, and consists of dots and lines. The geometry is the topology of the computer network.
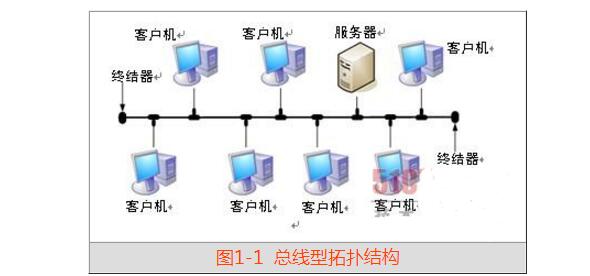
The bus topology is a topology based on multi-point connection. It connects all devices in the network directly to the common transmission medium through corresponding hardware interfaces. The bus topology uses a common channel that all PCs can access. Each PC requires only one cable. In the bus topology, all online microcomputers are directly connected to the bus through corresponding hardware interfaces. The information of any node can be transmitted and propagated in both directions along the bus, and can be used by any node in the bus. receive. Because its information travels around, similar to broadcast stations, bus-type networks are also known as broadcast networks. The bus has a certain load capacity, therefore, the bus length has a certain limit, a bus can only connect a certain number of nodes. The most famous bus topology is Ethernet.
Bus layout features: simple and flexible structure, very easy to expand; high reliability, fast network response; low equipment, low price, easy installation and use; strong ability to share resources, very easy to broadcast work, that is, a node to send all Nodes are acceptable.
The device connected at both ends of the bus is called a terminator (end impedance matcher, or terminator), and it is mainly matched with the bus line to absorb the energy of the transmission end to the maximum extent so as to prevent the signal from reflecting back to the bus and causing unnecessary interference. . The bus-type network structure is the most widely used structure at present, and it is also the most traditional kind of mainstream network structure. It is suitable for applications in the field of information management systems and office automation systems.
Each node in the ring network is connected to a closed ring-shaped communication line connected end to end through a loop interface. That is, each PC is connected. The data passes through each PC directly to the destination along the ring. Any node on the ring is You can request to send information. Once approved, the request can send information to the loop. The data in the ring network can be either unidirectional or bidirectional. The delay time for information on each device is fixed. Because the ring is public, the information sent by one node must pass through all ring interfaces in the ring. When the destination address in the information flow matches the address of a node on the ring, the information is received by the ring interface of the node, and the information is continued. The flow goes to the next-loop interface and it flows back to the loop interface node that sent the message. Especially suitable for real-time control of LAN systems. In the ring structure, each PC is connected to two other PCs. Each PC's interface adapter must receive data and transmit it to another. Because of the cable between the two PCs, good performance can be achieved. The most famous ring topology network is the Token Ring.
3, tree topologyThe tree topology evolved from the bus topology and resembles an inverted tree, with the root at the top and branches below the root, and each branch can also be subbanded. It is an extension of the bus structure. It is formed by adding branches on the bus network. The transmission medium can have multiple branches, but it does not form a closed loop. The tree network is a layered network, and its structure can be symmetrical. Fixed, with a certain fault tolerance, generally a branch and node failure does not affect the work of the other branch node, any node sent information can be transmitted throughout the transmission medium, but also broadcast network. Generally, the links on the tree-like network are relatively specific and can be expanded without any changes to the original network. It is a hierarchical structure. Nodes are connected in layers. Information exchange is mainly carried out between upper and lower nodes. Data exchange between adjacent nodes or peer nodes is generally not performed. The entire cable is connected into a tree type. Each branch of the tree branches has a computer at every point. The advantage of data transmission in turn is that the layout is flexible but the fault detection is complicated. The PC ring does not affect the entire system.
4, star topologyThe star topology is a radiating interconnected structure that connects several peripheral nodes with the central node as the center. Each node is connected to the central node through point-to-point. The central node implements a centralized communication control strategy. The central node is quite complicated and the burden is heavy. This kind of structure is suitable for the local area network, especially the local area network that connects in recent years mostly adopts this kind of connection way. This type of connection uses twisted pair or coaxial cable for the connection. A central computer is placed in the center. A PC is placed at the end of each arm. All data packets and messages are communicated through the central computer. Each PC except the central computer has only one connection. This structure requires a large number of cables. The star topology can be seen as a one-level tree structure and does not require multi-layer PC access rights contention. Star topology is more common in network cabling.
Networking is based on a star topology, in which any two sites must communicate through the central node. The main functions of the central node are: establishing a physical connection for the devices that need to communicate; maintaining this path for the communication between the two devices; and removing the channel when the communication is completed or unsuccessful. In the File Servers/WorkstaTIon LAN mode, the central point is a file server that stores shared resources. Due to this topology, the center point is connected to multiple workstations. In order to facilitate centralized connection, hubs (HUBs) are currently used.
5, mesh topologyThe mesh topology is also called a random structure, and the connections between the nodes are arbitrary and irregular. Is to connect multiple subnets or multiple LANs to form a network topology. In a subnet, hubs, repeaters connect multiple devices, and bridges, routers, and gateways connect subnets. According to different networking hardware, there are three main network topologies.
Bus topology advantages and disadvantages :(1) The network structure is simple, the insertion and deletion of nodes is convenient, and the network expansion is easy.
(2) The equipment is small, the cost is low, and it is easy to install and use.
(3) High reliability. Because the failure of a single node does not involve the entire network.
Disadvantages:(1) The bus transmission distance is limited and the communication range is limited.
(2) Fault diagnosis and isolation are more difficult. Fault isolation is difficult. When the node fails, isolation is still more convenient. Once the transmission medium fails, the entire bus needs to be cut off.
(3) Data collisions are prone to occur, and circuit contention is more serious. Distributed protocols do not guarantee the timely delivery of information and do not have real-time capabilities. Sites must have media access control capabilities, which increases the site's hardware and software overhead.
(4) Distributed protocols do not guarantee the timely delivery of information and do not have real-time capabilities. Sites must have media access control capabilities, thereby increasing the site's hardware and software overhead.
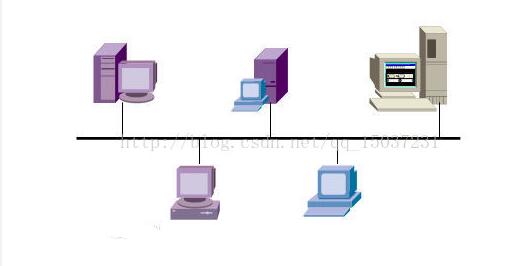
The bus topology is applicable to local area networks with a relatively small number of computers. Usually, this type of local area network has a transmission rate of 100 Mbps. Coaxial cables are used for the network connection. It is mainly suitable for small-scale sites such as homes and dormitories. Bus topology has been popular for some time. The typical bus LAN has Ethernet.
Floating Board To Board Connector
FLOATING Board to Board Connector
FLOATING Board-to-board (BTB) connectors as the name indicates is used for connecting circuits board together. This kind of connectors are suitable for stacking circuits boards one over another. Flat flexible cables can be avoided using these kinds of connectors; moreover it makes the entire unit more compact. The commonly used BTB connectors are SMT connectors and Berg Strip. We will discuss about them in detail in the following section.
SMT CONNECTOR
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) connector is a commonly found board-to-board connector in advanced circuit boards. As the name indicates this connector is available only in surface mount model. It is carefully mounted on to the solder pads on the surface of the PCB.
SMT connectors are ideal candidate for miniaturization due to their small area of occupancy and stacking height. They are suitable for double layered or multilayered PCBs. They are designed for high performance and reliability.
They commonly found in advanced circuit boards in networking equipment, telephones, mobile phones, computers and other consumer electronics.
Floating Board to Board Connector
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com