Basically, the main function of the LED driver is to convert the input AC voltage source into an output voltage that can follow the LED Vf (a current source that changes in forward voltage drop. As a key component in LED lighting, the quality of the LED driver directly affects To the reliability and stability of the overall luminaire. This article starts from the LED driver and other related technologies and customer application experience, and analyzes the failures of the luminaire design and application:
1. The range of variation of LED lamp bead Vf is not considered, resulting in low efficiency of the lamp and even unstable operation.
The load end of the LED luminaire is generally composed of a number of LEDs connected in series and parallel, and its working voltage is Vo=Vf*Ns, where Ns represents the number of LEDs connected in series. The Vf of the LED fluctuates with temperature fluctuation. In general, at a constant current, Vf becomes low at a high temperature, and Vf becomes high at a low temperature. Therefore, the operating voltage of the LED lamp load corresponds to VoL at high temperature, and the working voltage of the LED lamp at low temperature corresponds to VoH. When selecting an LED driver, consider that the driver output voltage range is greater than VoL~VoH.
If the maximum output voltage of the selected LED driver is lower than VoH, the maximum power of the luminaire may not reach the actual power required at low temperature. If the lowest voltage of the selected LED driver is higher than VoL, the driver output may exceed the working range at high temperature. Unstable, the lamp will flash and so on.
However, considering the overall cost and efficiency, we can't blindly pursue the ultra-wide output voltage range of LED drivers: because the driver voltage is only in a certain interval, the driver efficiency is the highest. After the range is exceeded, the efficiency and power factor (PF) will be worse, and the driver output voltage range is designed to be too wide, resulting in increased cost and inefficient optimization.
2. Power reserve and derating requirements are not considered
In general, the nominal power of the LED driver refers to the measured data under the rated environment and rated voltage. Considering that different customers have different applications, most LED driver suppliers will provide power derating curves (common load vs ambient temperature derating curve and load vs input voltage derating curve) on their own product specifications.
As shown in Figure 1, the red curve represents the power derating curve of the LED driver's load as a function of ambient temperature at 120Vac input. When the ambient temperature is lower than 50 °C, the drive allows 100% full load. When the ambient temperature is up to 70 °C, the drive can only reduce the load to 60%. When the ambient temperature changes between 50-70 °C, the drive load will follow. The temperature rises and decreases linearly.
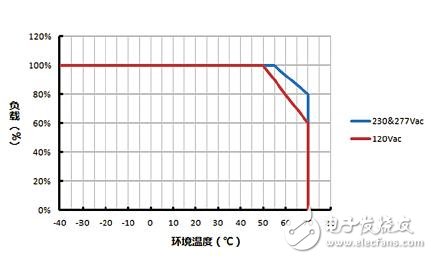
Figure 1 Power derating curve of load vs ambient temperature
The blue curve shows the power derating curve of the LED driver's load as a function of ambient temperature at 230Vac or 277Vac input. The principle is similar.
As shown in Figure 2, the blue curve shows the derating curve of the LED driver's output power as a function of input voltage at an ambient temperature of 55 °C. When the input voltage is 140Vac, the load of the driver allows 100% full load, and the input voltage is lowered. If the output power is constant, the input current will rise, resulting in increased input loss, reduced efficiency, and increased device temperature. May exceed the standard and may even cause device failure.
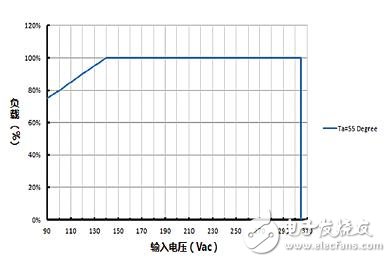
Figure 2 Power derating curve of load vs input voltage
Therefore, as shown in Figure 2, when the input voltage is less than 140Vac, the output load of the driver is required to decrease linearly as the input voltage decreases. After understanding the derating curve and the corresponding requirements, the LED driver should be considered and selected according to the actual ambient temperature and input voltage, and the derating margin should be appropriately set.
3. Do not understand the working characteristics of LED
Some customers have requested that the input power of the lamp be a fixed value, fixed by 5% error, and the output current can only be adjusted to the specified power for each lamp. Due to the different working environment temperatures and lighting times, the power of each lamp will vary greatly.
Customers make such requests, despite their marketing and business factor considerations. However, the volt-ampere characteristic of the LED determines that the LED driver is a constant current source, and its output voltage varies with the LED load series voltage Vo. The input power varies with Vo when the overall efficiency of the driver is substantially unchanged.
At the same time, the overall efficiency of the LED driver will increase after thermal balance. Under the same output power, the input power will decrease compared to the startup time.
Therefore, when the LED driver application needs to formulate the requirements, it should first understand the working characteristics of the LED, avoid introducing some indicators that do not conform to the principle of the working characteristics, and avoid the indicators far exceeding the actual demand, and avoid excessive quality and waste of costs.
Sanitation dispenser,it can automatically receive the signal to turn on the switch to the machine when the person reaches out the hand, so that the work sprays disinfectant or foam.
There are two working modes: automatic setting time and random time. It can be placed in toilets, kitchens, office buildings, hospitals, banks and other places.Suitable for a variety of viscous liquids, such as hand soap, detergent, disinfectant, sunscreen, etc. It can be placed in toilets, kitchens, office buildings, hospitals, banks and other places.

Sanitizer Dispenser,Hand Sterilizer Dispenser,Wall Mounted Hand Sanitizer,Automatic Hand Sanitizer Dispenser
Taishan Jie Da Electrical Co., Ltd , https://www.ts-jieda.com