From April 9th ​​to the end of March 2018, a Cisco high-risk vulnerability CVE-2018-0171 was attacked by hackers during the Qingming small long holiday. Many organizations in China tried to evade the configuration file, and the security device was in name only. This vulnerability affects the underlying network devices, and the vulnerability PoC has been exposed and is likely to pose a major threat.

CVE-2018-0171 vulnerability details
Cisco released a security announcement on March 28 stating that there is a remote code execution vulnerability CVE-2018-0171 for Cisco IOS and IOS-XE software Smart Install Client (with the Cisco Smart Install Management protocol enabled and the client mode), CVSS scores up to 9.8 Points (total score 10 points). An attacker can remotely send malicious packets to the TCP port 4786, triggering a target device's stack overflow vulnerability to cause the device to deny service (DoS) or execute arbitrary code remotely.

On March 29, 2018, China's National Information Security Vulnerability Sharing Platform (CNVD for short) included the vulnerability, numbered CNVD-2018-06774. CNVD describes the vulnerability as:
Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and mirror management function that provides zero-configuration deployment for switches that are newly added to the network. It implements the process of automating initial configuration and operating system image loading, and also provides configuration file backup functions. A remote command execution vulnerability exists in Cisco Smart Install that allows an attacker to send well-crafted malicious packets to the remote Cisco device's TCP 4786 port without requiring user authentication, triggering a vulnerability that allows the device to remotely execute Cisco system commands or denial of service (DoS).
According to the announcement issued by CNVD, the scale of the global Cisco Smart Install system is 143,000. According to the distribution of countries, the top three users are the United States (29%), China (11%) and Japan (6%).
Confirm the affected equipment:
Catalyst 4500 Supervisor Engines; Cisco Catalyst 3850 Series Switches; Cisco Catalyst 2960 Series Switches.
The following devices that contain the Smart Install Client may be affected by the vulnerability:
Catalyst 4500 Supervisor Engines;Catalyst 3850 Series;Catalyst 3750 Series;Catalyst 3650 Series;Catalyst 3560 Series;Catalyst 2960 Series;Catalyst 2975 Series;
IE 2000;IE 3000;IE 3010;IE 4000;IE 4010;IE 5000;
SM-ES2 SKUs; SM-ES3 SKUs; NME-16ES-1G-P; SM-X-ES3 SKUs.
More than 200,000 routers worldwide are affected
Initially, researchers believe that the vulnerability can only be exploited by hackers on the same network.
On April 5, 2018, the Cisco Talos team issued a blog post saying that hackers have exploited this vulnerability to attack critical infrastructure. The team through the search engine Shodan found that about 250,000 vulnerable Cisco devices opened the TCP port 4786, potentially exposing about 168,000 systems. When Cisco issued a vulnerability warning, its researchers identified about 8.5 million devices using this port at the first time, but it was not possible to determine whether Smart Install functionality existed on these systems.
Iran, Russia are the first to be attacked
On April 6, 2018, the hacker group "JHT" took the lead in attacking computer infrastructure in Russia and Iran using Cisco's Smart Install vulnerability CVE-2018-0171, affecting Internet service providers, data centers, and several websites. Hackers use this vulnerability to reset the router to the default configuration and display information to the victim.
The attacker used this vulnerability to attack the Cisco server. Subsequently, the router's configuration file "startup-config" is overwritten and the router is restarted, which in turn leads to a network outage. In addition, the administrator also discovered that the router's startup-config file was changed to a warning message: "Do not interfere with our election...-JHT". In addition to disabling devices and letting devices crash, the organization also left a picture of the American flag.

The Talos team believes that the attack was related to the warning issued by the US Computer Emergency Response Team in March 2018 (the Russian government targeted energy and other critical infrastructure industries). It is speculated that this is exactly what the hacking organization has responded to. The attackers said they just wanted to pass information. Experts speculate that this large-scale cyber attack is likely to be initiated by a civil hacking organization to express its dissatisfaction with Russia’s interference in the US election.
The hacker group "JHT" disclosed to the media that they have scanned many countries' vulnerable systems, but they only target Russian and Iranian routers. The hacker group also stated that it fixed the Smart Install vulnerabilities found on US and UK routers by issuing the “no vstack†command.
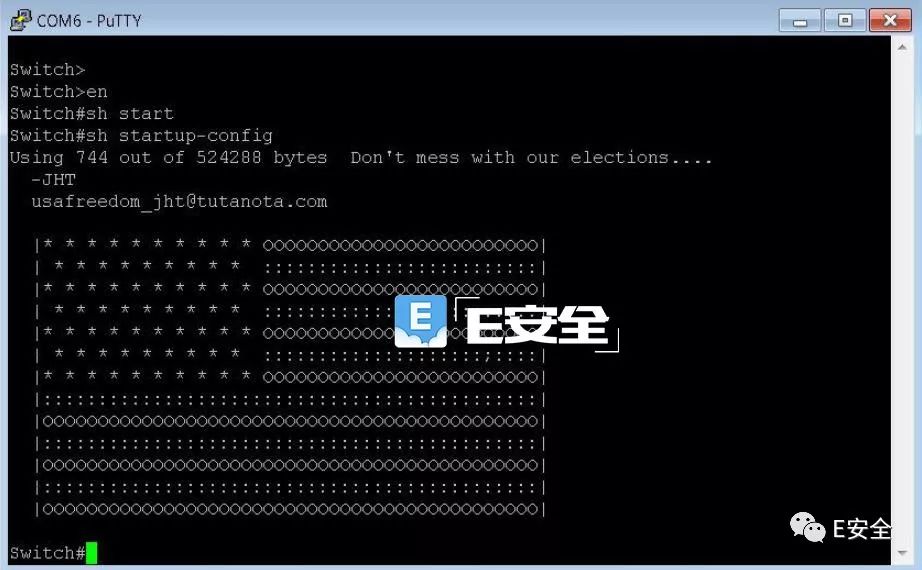
The startup configuration of the attacked router
About 14,000 Taiwanese Affected Equipment
According to Reuters, the Iranian Ministry of Communication and Information Technology said that more than 200,000 routers worldwide are affected:
Iran: 3,500 units;
United States: 55,000 units;
China: 14,000 units.
Iran’s Minister of Communications and Information Technology Mohammad Javad Azari-Jahromi stated on Twitter that at 9:12 PM Eastern Time on April 6, 2018, 95% of Iran’s affected routers have resumed normal service. Iran’s IT Minister Mohammed Jawad Azali Jahrommi said that the main impact of the attack is Europe, India and the United States.
However, on April 8, 2018, a number of Chinese agencies also received similar attacks.
How to check?
Remote self-check:
Method one: Check whether the target device is enabled with the 4786/TCP port. If it is enabled, it may be affected. For example, use nmap to scan the target device port: nmap -p T:4786 192.168.1.254
Method Two: Use the Cisco-provided script to detect whether to open the Cisco Smart Install protocol, which may be affected if it is turned on. # python smi_check.py -i 192.168.1.254[INFO] Sending TCP probe to targetip:4786[INFO] Smart Install Client feature active on targetip:4786[INFO] targetip is affected.
Local self-check (need login device):
Method 3: You can use the following command to confirm whether to enable the Smart Install Client function: switch>show vstack configRole: Client (SmartInstall enabled) Vstack Director IP address: 0.0.0.0switch>show tcp brief allTCB Local Address Foreign Address (state) 0344B794 *. 4786 *.* LISTEN0350A018 *.443 *.* LISTEN03293634 *.443 *.* LISTEN03292D9C *.80 *.* LISTEN03292504 *.80 *.* LISTEN
Method 4: switch>show version Save the echo content in a.txt and upload it to Cisco's Cisco IOS Software Checker for detection. Detection address: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/softwarechecker.x
Temporary Disposal Measures (Close Agreement)
Switch#conf tswitch(config)#no vstackswitch(config)#do wrswitch(config)#exit
Check that the port is turned off:
Switch>show tcp brief allTCB Local Address Foreign Address (state)0350A018 *.443 *.* LISTEN03293634 *.443 *.* LISTEN03292D9C *.80 *.* LISTEN03292504 *.80 *.* LISTEN
Air Glow Pro Vape Pen,Vape Pen Battery Charger,Electronic Cigarettes Kits,Disposable Electronic Cigarettes Kits
Shenzhen Aierbaita Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.aierbaitavape.com