Modern mobile phones are basically built-in battery management chips, responsible for battery charging, protection, measurement and other work. For the charging power supply, the requirements will be relatively low. Generally, the original charger of our mobile phone is a compact small switching power supply.
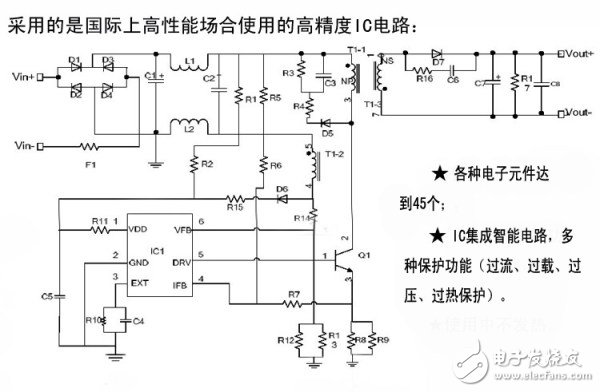
This is a typical switching power supply circuit that is used to convert the 220V mains into a low voltage that we need. The output voltage is generally between 5 and 5.5V, and the output current is between 0.5A and 3A. Of course, there will be more output voltage files to support the latest fast charge specification, which we will talk about later.
However, the nominal voltage of the rechargeable lithium polymer battery in the mobile phone is 3.7V, and the discharge range is generally 3.2-4.2V. The external power supply cannot be directly connected to the battery for charging, which causes the battery current to be too large, and the overvoltage , thus damaging the lithium battery.
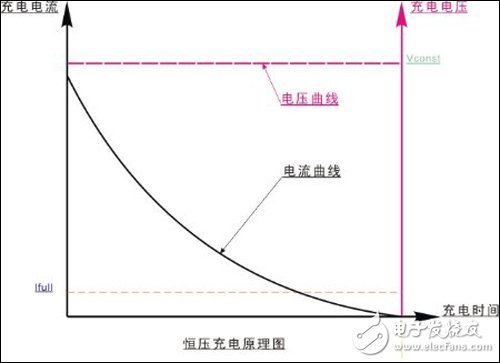
Even if the voltage is reduced to the voltage of a suitable battery, the lithium battery cannot use this constant voltage charging method. After all, the lithium battery is more delicate. In order to control the heat, prolong the life and increase the safety, most types of batteries are now safer and more constant. Stream charging method.
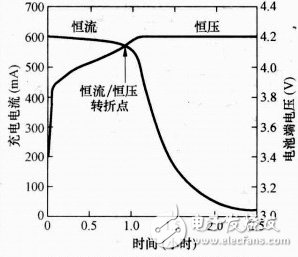
The constant current charging method can control the heat well, and the battery will be safer and more reliable.
This part of the function is completed by the built-in battery management chip of the mobile phone, because the conversion of voltage and current is impossible, especially on the mobile phone with high current charging, it will obviously feel that the mobile phone will generate heat, which is inevitable. Because there is loss after all, the loss is even heat. Conversion efficiency can only be reached infinitely close to 100% and is not possible.
When it comes to mobile phones of different brands, there is still something to say, this is the identification circuit.
This part of the thing is directly connected to the charger's USB output interface, for the phone to identify whether the charger meets the requirements.
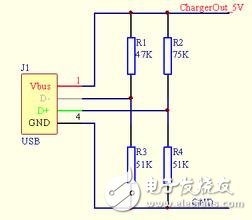
This is the typical identification circuit of Apple's mobile phone. It uses the resistance method. By detecting the voltage value on the D+ D- foot, it determines the charging current of the device and determines whether the device can be charged.
Without this circuit, the device will only work at a minimum. Samsung and other tickets for Android phones are similar, but the program is simpler and more rude, D + D- directly connected. The two schemes are actually compatible on both sides, but the result of the hybrid plug-in is that it can only be charged with a small current. According to the previous actual test experience, it is probably between 100-200 mA and cannot be charged at a large current.
Off-topic, under the same charging current, a mobile phone that feels high heat may actually have a better heat dissipation design, because in the case of almost hot, the heat conduction is fast to ensure a lower core temperature. Therefore, it is not necessary to be too entangled to charge and heat up. When the heat dissipation design is reasonable, the heat is large and the charge is fast, and the heat is small and the charge is slow, which is basically universal.
12v 11Ah motorcycle battery
Starlight Power Industrial Company Limited , https://www.starlite-power.com