With the gradual maturity of Wi-Fi technology, various Wi-Fi terminals such as laptops, PDAs, dual-mode mobile phones, Wi-Fi-enabled game consoles, and instant digital cameras have sprung up in the market. It is getting lower and lower. Compared with several other wireless communication technologies, the advantages of Wi-Fi technology are very obvious. Compared with 2G/3G, Wi-Fi bandwidth is 10 times that of 3G, and the cost of networking is much cheaper than 3G. Although the WiMax technology is advanced, the terminal price remains high, and the license policy is unclear, which restricts its development. Therefore, Wi-Fi is a wise choice as a complement to 3G data services. Major operators at home and abroad have stepped up the construction of Wi-Fi LAN/Metropolitan Area Network (WLAN), which has set off a boom in hotspots, hotspots and even wireless cities, and many companies are also involved. However, while increasing efforts to invest in wireless WLAN construction, many enterprises are also faced with many real problems: how to quickly deploy business? How to deploy with the wired broadband metropolitan area network? How to achieve effective management? It is precisely because of these problems that enterprises face greater risks in the networking process. They are worried that the initial investment is too large, and they are not proportional to the income. At the same time, they are afraid that the maintenance cost will be too high and they will be overwhelmed. Is there a good solution? Perhaps the idea of ​​this program can help you solve this problem.
Manageable broadband enterprise internal wireless network solutionHow to provide better service in WLAN, an open network is a problem that must be considered when constructing a WLAN network. It must achieve rapid deployment and protect user investment. At the same time, it must implement network traffic management and provide future-oriented device upgrade solutions for WLAN. The network provides a comprehensive and viable solution. In order to achieve this goal, the dual-mode AP networking mode, which is fat and thin, may be the best choice at present, which can solve the problems of excessive initial investment and difficulty in upgrading in the networking process.
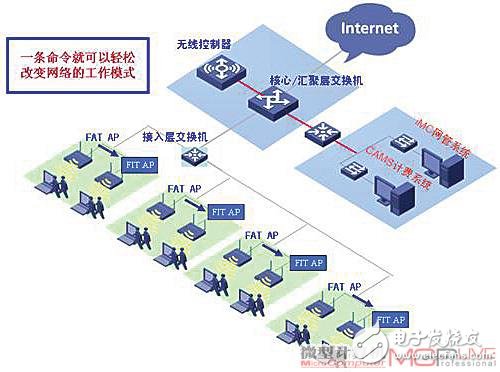
For users with insufficient investment budget, the dual-module solution that is fat and thin can effectively protect the user's investment. The new AP can support free transition between fat/thin APs, thus achieving a smooth transition from "fat" to "thin". In the initial stage of network construction, the fat AP mode is conducive to the rapid deployment of services. As the network scale continues to expand, the fat AP is upgraded to the thin AP mode by commands, and then the wireless controller is added to achieve a smooth transition, thereby achieving unified management and deployment of the AP device, and protecting the upfront investment. Currently, this networking solution is being adopted by most networking users.
Tips: What are fat APs and thin APs?
An access point (AP) is also called a wireless bridge or a wireless gateway, which is also called a "thin" AP. Its transmission mechanism is equivalent to a hub in a wired network, and it continuously receives and transmits data in a wireless local area network; any PC with a wireless network card can share resources of a wired local area network or even a wide area network through an AP. In theory, when a wireless AP is added to the network, the network coverage can be expanded exponentially, and more network devices can be accommodated in the network.
The so-called "fat" AP is actually a wireless router. Unlike a pure AP, a wireless router generally has two interfaces, WAN and LAN, in addition to the wireless access function. Most of them support DHCP server, DNS and MAC address cloning, and VPN (Virtual Private Network) access, firewall and other security functions.
Redundancy schemeWhen the fat AP mode is switched to the thin AP mode, the newly added wireless controller is faced with a failure or failure that causes the entire wireless network to be paralyzed, so the wireless controller must be redundant. However, the cost of purchasing a wireless controller is also difficult for many users to accept. The thin AP restores the working mode of the fat AP when the wireless controller fails. As a solution for emergency work, it becomes a key to solve this problem, but the premise is All APs must support fat/thin mode conversion, which is the key to ensuring program scalability and redundancy.
Others
Others
ATKCONN ELECTRONICS CO., LTD , https://www.atkconn.com