Everything grows by the sun. We are familiar with the demand for light from terrestrial animals. So is the use of light for aquatic fish the same as that of terrestrial animals? Where is its special point?
Fish feeding, breeding, predation, escaping from predators, clusters, etc. are the main behaviors in the natural environment, and each behavior is closely related to illumination. During the evolution of billions of years, fish receives light signals through the photoreceptors of the retina and the pineal gland, simultaneously sensing and adapting to the light environment of natural habitats. Over time, a unique visual physiological structure is formed.

Light in the sea

The eyes of Hongji Oriental
The basic structure of the fish's eyes is similar to that of the higher vertebrates, and the absorption spectrum ranges from 430 to 620 nm. The inner retina of the fish eye is composed of sensitized cone cells and rod cells. Its cone cells are similar to the human eye cone vision function, which accepts bright light, has the ability to distinguish color and fine resolution; the rod cells receive weak light, high light sensitivity, no color discrimination and fine resolution. Living in a well-lit environment, the upper water body of the fish is developed with cones, and even the retina is composed entirely of cone cells; the retina of the night-out deep-sea fish has few cones, and even the retina is completely Rod cell composition.
The short-wavelength blue light in visible light can be distributed in seawater up to nearly 100 meters. In the near-shore fresh water with more phytoplankton and particulate matter, the long-wavelength red-orange spectrum of visible light dominates, generally speaking, the fish retina The visual pigments are consistent with the peaks of the spectrum of the inhabited waters. Therefore, the fish spectral sensitivity curve of deep-water activities is sensitive to blue-green light in the short wavelength range, while the light absorbed by fish living in nearshore and fresh water is biased in the long wavelength range. For example, the blue-spotted garfish perched on the surface of 0-10m, and red light stimulates the development of the gonads. Then the aquatic worker chooses the red orange spectrum when raising seedlings. The black mites are commonly found at depths of 40-200 m, and the use of blue light significantly increases their food intake. Therefore, when artificially breeding this fish, it is necessary to use blue light.
Breeding with light color

Fish color light color experiment
Japanese squid is active in water layers with a water depth of 25 meters or more. This part of the green light spectrum is more. Therefore, under the green light, it forms a stable fish group well, so the LED green light attracting fish lamp is very popular among fishermen. Sardines, squid, squid, blue scorpionfish, squid, etc. all have strong phototaxis, and the light trapping effect is very good. At the time of fishing, the use of red and yellow light to induce a large range of fish to gather in a relatively small range is based on the slow swimming and slow behavior of some offshore fish.
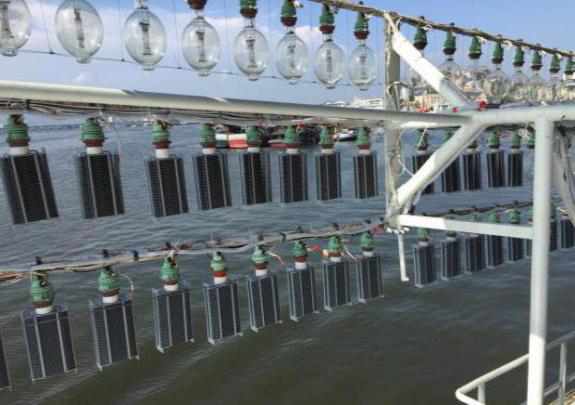

Fishing light on a fishing boat

Fish light lit at night
If the squid group is illuminated with blue and white light, it will panic and swim, and the vertical swimming is very intense. This is because many ferocious carnivorous fish have a grayish white abdomen, grayish blue light or large shadows in the field of vision, and inconspicuous flashing light indicates the coming of the disaster.
Fish are clustered in response to specific light colors. The color and pattern of the fish are various. For example, the squid has a golden brown bronze enamel, and a black spotted pebbles. The fish that live in the cluster often rely on the color of the fish in the group to identify each other and determine their position.
Sexually mature fish, the body color is generally brighter, such as Atlantic salmon, migratory to the spawning ground, the external silver color disappears, the red and orange spots and markings on the male body become red fish. At this time, the male and female fish are easy to get close to each other and breed offspring because they wear a "marriage dress".
Many organisms depend on the growth of the annual photoperiod to grow, develop and multiply. For fish, the long photoperiod is an important "time-sense factor". Studies have shown that the photoperiod has an important influence on the growth and reproduction of gem cynomolgus, squid, gilthead, and Atlantic salmon. Knowing this, in aquaculture production, photoperiod regulation can accelerate or delay the start time of such fish gonads.

Atlantic salmon

Cultured gonads of Atlantic salmon
Knowing the usefulness of light to fish, modern aquaculture can effectively create a suitable light environment, induce and regulate the biological behavior of fish growth and reproduction, and thus achieve the production goal of “quality, high yield, ecology and safety†of the aquaculture industry.
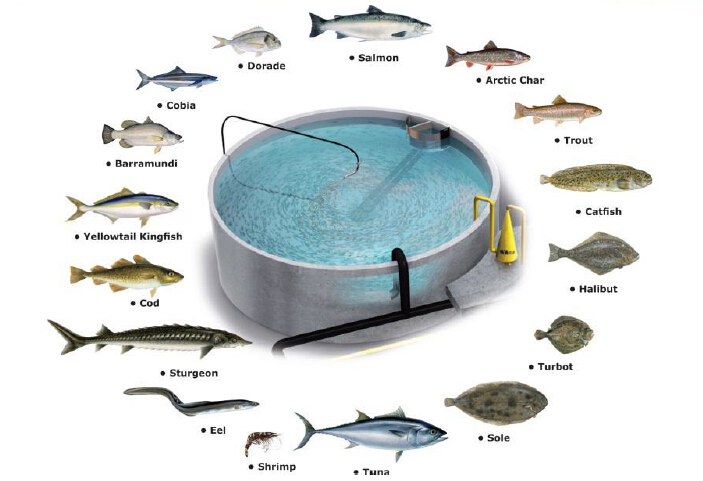
Aquaculture fish species

Aquaculture workshop

Experiment in the breeding workshop
Editor: Yan Zhixiang
Uv Curving Glass,Tempered Glass Screen Protector,Film Cutting Machine,Uv Curing Protector Screen
Shenzhen TUOLI Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hydrogelprotectors.com