introduction
He is the only German company among the four industrial robots. He is one of the few giants acquired by Chinese capital in the field of industrial automation. He has more than a hundred years of history, but he has always been at the forefront of innovation. He, KUKA, is a global leader in industrial robots and is regarded as one of the core companies of German Industry 4.0.
At the beginning of 2017, KUKA announced the completion of the transaction with Midea, and the majority of the shares were sold. It has also become the largest case of cross-border mergers and acquisitions in the industrial automation industry.

Today, it has been more than a year since the two sides reached an acquisition in January last year. At the end of March this year, KUKA released its first annual report after being acquired by Midea. What is the real situation of this company? What is the dynamic of each business segment this year? How is KUKA changing in the Chinese market?
With these questions in mind, let us briefly review the history and business branches of KUKA, and take you through this latest annual report to understand the changes in KUKA during the year.
1. The income has increased greatly, but the profit rate has declined.
According to the KUKA 2017 Annual Report. The company's total order delivery volume in 2017 was 3.6 billion euros, up 5.6% year-on-year; total sales were 3.5 billion euros, up 18% year-on-year; EBIT was 4.3%, down from 4.7% in 2016, net income was 88.2 million euros, year-on-year. Growth of 2.3%.
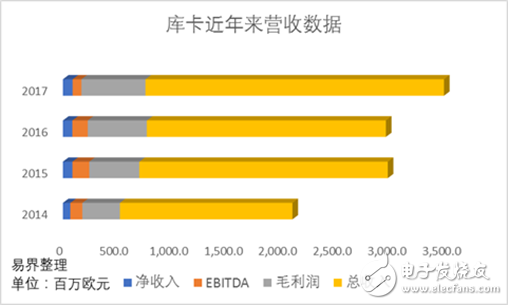
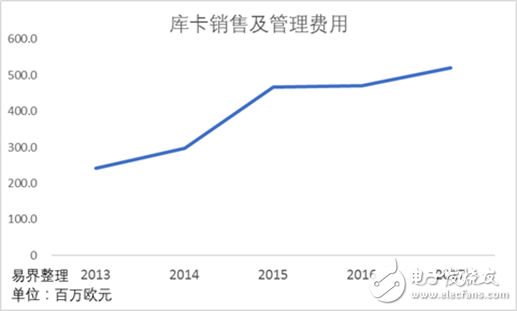
It can be seen that KUKA has experienced tremendous growth in total revenue, but the profit margin has declined. Part of the reason is that in 2017, KUKA conducted a series of research and development and investment in the field of Internet of Things and 3D software, while KUKA's sales and management costs also increased significantly. These factors all affect the company's profit margins.
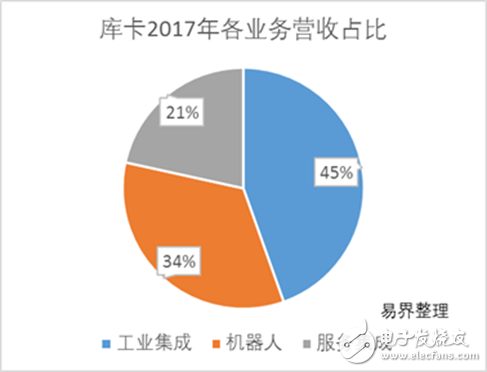
KUKA's main business is divided into three sections. Unlike ABB's involvement in the electrical grid, FANUC's involvement in CNC machines, Yaskawa's involvement in motors and other industrial equipment, KUKA is the only automation company among all four who are concentrated in the field of industrial robotics.
His main business is divided into: industrial automation machinery body and core components (hereinafter referred to as "robot plate"), intelligent factory systems in industrial scenarios (hereinafter referred to as "industrial integration"), automation solutions for the medical and logistics industries. (hereinafter referred to as the "Service Integration Board").
2. Robot business: electronic product driver, won a number of new cooperation
Since 2016, the global industrial robot application industry is gradually moving from automobiles to electronics. The latest announcement from KUKA is also a good example of this: the KUKA robot segment is mainly benefiting from the growing demand for electronic production lines.
In the application field of KUKA robots in 2017, the proportion of the automotive sector dropped sharply from 46.4% in 2016 to 35.4%, while the proportion of applications in other industrial sectors rose from 36.6% to 45.3%. The service sector has not changed significantly, rising from 17.0% to 19.3%.
Overall, the KUKA robot segment revenue was 1.2 billion euros, up 20.8% year-on-year compared to 993 million euros in 2016, with an EBIT rate of 11.1%, an increase from 10.1% in 2016. At the same time, it has a very high ROCE of 50%.
As the core business, KUKA has gained a lot in the robotics sector in 2017. It not only signed a comprehensive cooperation strategy agreement with Bosch, but also won the best supplier of GE powertrain and body shop equipment, and also obtained Siemens medical equipment in the medical field. Technical authorization.
3. Integrated business: bet on medical and logistics, whether it can stand out under fierce competition
Thanks to the strong demand in the new energy field, KUKA's industrial integration in 2017 mainly comes from battery production, and sales have also increased by a certain amount, but the net profit is not optimistic.
In the fourth quarter, the department's EBIT was negative at 37.32 million euros, which was only 17.8 million euros for the whole year, a significant drop of 80.5% from the previous year's 91.3 million. The EBIT rate has dropped significantly from 6.5% in 2016 to 1.1%.
There are two official reasons given by KUKA, one is affected by several individual projects, and the other is the loss caused by the Group's income-increasing measures. It is not difficult to imagine that the strong demand for the industrial system integration industry has created a severe competitive environment, which led to KUKA paying so much for a single project in order to seize the market.
In 2015, in order to better manage the automation solution business of non-industrial application scenarios such as medical, warehousing, logistics, etc., which is what we call the service integration section, KUKA separates this part of the business and let the subsidiary company Swisslog carry out management.
In the past three years, KUKA’s new industry’s sales growth has been evident: 491 million euros, 624 million euros, and 768 million euros. This part of the business mainly uses chain pharmacies as the main sales target. This part of the EBIT rate is relatively stable and has not changed significantly in the past three years.
But one thing worth noting is that this part has a very low return on ROCE, only 3%. It can be seen that the cost of capital to support the development of this part of the business is extremely high. Compared with other businesses, this part of the business has a large number of employees. It can be seen that KUKA is preparing to fight a long-term battle with competitors in the new application field of robots.
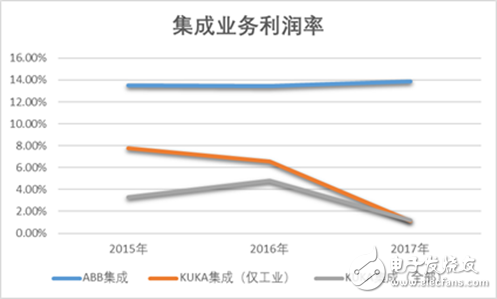
And from the perspective of profit margins, there is still a big gap between KUKA's integrated business and ABB in the short-term. However, with the blessing of the United States, KUKA still has a great possibility to obtain more integration orders in the Chinese market in the future.
4. Chinese market performance and synergy
After a brief review of the business segment of KUKA, let us look at the performance of KUKA in the Chinese market after the acquisition of the US, and future development plans.
When the acquisition transaction was reached, both parties were full of confidence and had high expectations for synergies.
In the 30 years before the cooperation with the United States, KUKA officially entered the Chinese market in 1986. Just then, it gave a robot to FAW Trucks, the first industrial robot in China to be used in manufacturing.
After entering the Chinese market, KUKA succeeded in making domestic auto companies such as Dongfeng and Changan the first loyal customers.
For KUKA, the Chinese market has always been the main market for KUKA, and it is also the home base of the United States. The entire Chinese robot market is a huge cake for KUKA. In 2016, KUKA occupied the second place in the Chinese industrial robot market.
In the 2017 annual report, KUKA reported that its revenue in the Chinese market accounted for approximately 20%. At the same time, benefiting from the influence of national plans such as “Internet +â€, 13th Five-Year Plan, and China Manufacturing 2025, KUKA predicts that the Chinese market will increase at a compound annual growth rate of 20%, mainly in the automotive and electronic products. .
At the same time, KUKA, which is married to Midea, has also stepped up its pace of integrating China's business.
On March 22 this year, Midea Group announced that it plans to establish a joint venture with KUKA to undertake KUKA's China business.
In this transaction, KUKA plans to merge its business branches in China and establish a joint venture with Midea Group to undertake this part of the business. The shareholders of the joint venture will each hold half of the shares.
At the same time, KUKA will build a new production base in Shunde Science and Technology Park in China, and develop new products until the robot production capacity reaches 75,000 per year in 2024. Together with the existing production capacity, its total robot production capacity in China will reach 100,000 units per year.
In the end, based on the aforementioned results and the greater synergy brought about by the integration of the Chinese market, KUKA made a financial outlook in the annual report with a sales income of more than 3.5 billion euros and an EBIT rate of 5.5% in 2018.
We believe that Midea’s investment has a long-term return. KUKA will not only become the main driver of the transformation and upgrading of the United States, but also become the most important robot giant in the industrial robot industry in China in the future.

Expand reading: KUKA's century-old history and technical briefs Over the centuries, KUKA has created many of the world's first.
Founded in 1898 in Augsburg, Germany, KUKA initially focused on indoor and urban lighting and soon began to get involved in other areas.
In 1956, KUKA built the first automatic welding equipment for refrigerators and washing machines, and provided Volkswagen with the first multi-point welding line. In 1971, KUKA built the first welding line for robots in Europe for Daimler Benz.
In 1973, an industrial robot called FAMULUS was developed, which is also the world's first motor-driven six-axis robot. Since then, KUKA has opened up a journey of more than 40 years in the field of industrial robotics.
In 1996, KUKA's industrial robot research and development achieved a leap forward. The first PC-based control system developed by it began to be put on the market, thus creating a “real†era of mechatronics characterized by the perfect combination of software, control systems and mechanical equipment.
In 2007, KUKA launched KR TItan, which has a load capacity of 1000 kg and a range of 3,200 mm. It was the world's largest and most powerful six-axis industrial robot.
In 2013, KUKA launched the world's first collaborative robot LBR iiwa for industrial applications.
Today, with the rigorous spirit and exquisite craftsmanship of German companies, KUKA robots are widely used in the automotive, metallurgical, food, medical and plastic molding industries.
Why is it that the United States has to invest heavily in the acquisition of this German company, and what advantages does KUKA have over other robotics companies?
To put it simply, compared with similar enterprises, KUKA has the following three advantages: simple human-computer interaction, unrealistic fashion innovation, and core technology leading the industry.
First of all, one of KUKA's great strengths is its easy-to-understand operating software. Even if it is the first time that a fledgling apprentice worker uses it, he can basically get started in one day.
In the man-machine interface, KUKA is very simple. In contrast, the Japanese brand robots based on Yaskawa and FANUC have many control system keyboards, and the operation is slightly complicated.
Second, chasing new and fashionable is the label of KUKA. Looking at the appearance of the product alone, KUKA's products are much better than the other three.
Moreover, KUKA is not a traditional manufacturing company in terms of marketing.
This is a few years ago, when KUKA invited the famous table tennis player TImo Boll to shoot the advertisements of the man-made table tennis competition, you can also see one or two.
Most critically, KUKA has many advanced technologies that are leading the industry. One of them is its software-based security controller technology.
Major manufacturers in the field of industrial robots have their own safety technologies, such as ABB's SafeMove and FANUC's DCS. These safety controllers are implemented using hardware, and a safety control panel can be seen inside the control cabinet. There are very strict requirements for the authentication of the safety controller. Generally, the hardware will adopt the dual CPU configuration. Sometimes, the two CPUs are required to use different types of chips. The 1oo2 strategy is used. As long as the two CPU calculation results are inconsistent, the system will stop immediately. .
While KUKA uses a completely software-based approach, the KRC4 control system runs the SafeOS provided by K&W in two different cores of an x86 CPU and passes the safety certification with only one CPU.
It is no wonder that some insiders say that KUKA is the most "soft" vendor among the four.
It is also worth mentioning that KUKA is doing a good job in the field of heavy-duty robots. Among the robots above 120KG, KUKA and ABB have a large market share, while in heavy-duty 400KG and 600KG robots, KUKA The sales volume is the most.
RCA Cables can be used to connect a variety of audio and video devices, such as camcorders, to TVs or stereos to speakers. Most high-end camcorders have all three RCA jacks, so the signal entering or leaving the device goes through three separate channels-one video and two audio-resulting in a high-quality transfer. Lower-end camcorders usually have only one jack, called a stereo jack, which combines all three channels. This results in lower-quality transfers because the signal is compressed. In either case, RCA cables transmit analog, or non-digital, signals. Because of this, they cannot be plugged directly into a computer or other digital device. RCA cables connect amplifiers to all sorts of devices.
Ucoax OEM Cable Assembly RCA Cables
Quality of RCA Cables
Several factors affect the quality, price, and performance of RCA cables:
Materials: The connectors on RCA cables are often gold, silver, or copper. As you might expect, the gold connectors are the most expensive. They're also better than silver and copper connectors at preventing oxidation, but not as good at electrical conductivity. The silver connectors are best for electrical conductivity with the copper cables coming in a close second and the gold cables falling far behind. Other suitable materials are nickel, zinc, and tin.
Cable Length: Cable length has a negative effect on signal quality. Buy a cable that is only as long as you need it to make the connection for the best signal quality.
Shielding: A well-shielded cable delivers a better signal than one that lacks robust shielding.
The other end of the cable: If possible, match the material used in the other end of the cable to the material used in the connectors. Don't match tin with gold or silver with gold. Those combinations can cause problems because of an electrolytic reaction.
High Quality RCA Cables, Male to Male RCA Cable, RCA Cables for HDTV
UCOAX , https://www.jsucoax.com