Everyone knows that the cache has a great impact on the CPU, but few people know the specific effect. This article mainly introduces the difference between the 3m and 6m CPU level 2 caches, and discusses the impact of the cache on the CPU operating speed.
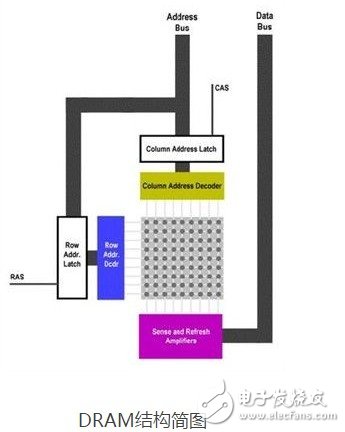
CPU cacheThe CPU cache (Cache Memory) is a temporary storage located between the CPU and the memory. Its capacity is much smaller than that of the memory but the exchange speed is much faster than that of the memory. The appearance of the cache is mainly to solve the contradiction between the CPU operation speed and the memory read and write speed, because the CPU operation speed is much faster than the memory read and write speed, which will make the CPU spend a long time waiting for the data to arrive or write the data RAM. The data in the cache is a small part of the memory, but this small part is about to be accessed by the CPU in a short time. When the CPU calls a large amount of data, it can be called in the cache first to speed up the reading speed.
What is the difference between 3m and 6m of CPU level 2 cacheThe higher the CPU cache, the higher the CPU grade rather than the lower the main frequency. Some high-end CPUs use the level 3 cache.
The cache of the CPU is generally matched with the processing performance of the CPU. The more CPU cache levels and the more capacity, the stronger the CPU performance, the more cache needs to be used.
The CPU cache is a temporary storage located between the CPU and the memory. Its capacity is much smaller than that of the memory but the exchange speed is much faster than that of the memory. The appearance of the cache is mainly to solve the contradiction between the CPU operation speed and the memory read and write speed, because the CPU operation speed is much faster than the memory read and write speed, which will make the CPU spend a long time waiting for the data to arrive or write the data into the memory .
Generally speaking, the CPU cache is divided into three levels of cache. Among them, the first level of cache appears the earliest. Due to the limitation of cost and manufacturing difficulties, the second level and the third level of cache have gradually developed. The difficulty and difficulty of the production of level 2 cache is higher than that of level 1 cache. Small, so the capacity is relatively larger, and the three-level cache is less difficult so the capacity is the largest. The content in each level of cache is part of the next level of cache. In addition, the third-level cache may not be included with all CPUs, and generally only high-end CPUs will come with it.
When the CPU wants to read a piece of data, it first looks in the first level cache, if it doesn't find it, then it looks up in the second level cache, if it still doesn't, it looks up in the third level cache or memory. Generally speaking, the hit rate of each level of cache is about 80%, which means that 80% of the total data volume can be found in the first level cache, and only 20% of the total data volume needs to be from the second level cache. , Level 3 cache or read in memory, it can be seen that Level 1 cache is the most important part of the entire CPU cache architecture.
In addition, the materials of the CPU cache are different at all levels. The first level cache uses the fastest SRAM (static RAM), the second level cache uses a relatively slower highly dynamic RAM (DRAM), and the third level cache also uses DRAM. Due to the difficulty of manufacturing the first level cache, the size of the second level cache generally distinguishes the high and low ends of the same core processor.
The impact of cache on CPU performance
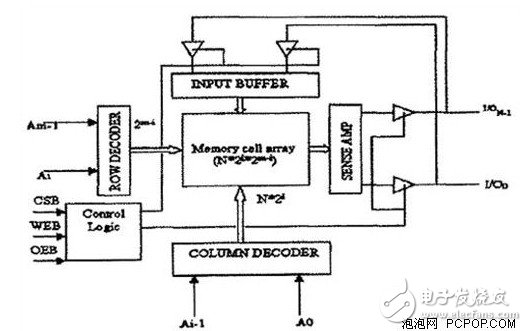
How much influence does the CPU cache have on the performance of the CPU? First of all, the editor will briefly introduce the CPU cache. The CPU cache (Cache Memory) is a small but high-speed temporary memory located between the CPU and the memory. It is usually composed of SRAM (Static Random Access Memory). Used to store data that is frequently used by the CPU, so that the CPU does not have to rely on slower DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory). But limited to its expensive cost, the general capacity is smaller than the memory.
SRAM structure diagram
The design idea of ​​the cache is to use a small amount of faster SRAM as the buffer between the CPU and the DRAM storage system. At first, it was outside the chip. In the 80486 period, this part of the SRAM was integrated into the chip, so it is also called on-chip. Cache.
The on-chip Cache is today's level one cache. The capacity of this part of the cache is very small, only 8KB in the 486 chip, and upgraded to 16KB in the Pentium high-end chip, and up to 32KB in the Power PC. Later, Pentium microprocessors improved the on-chip Cache, using data and dual-channel Cache technology to be very flexible and convenient, which greatly improved the performance of the microprocessor.
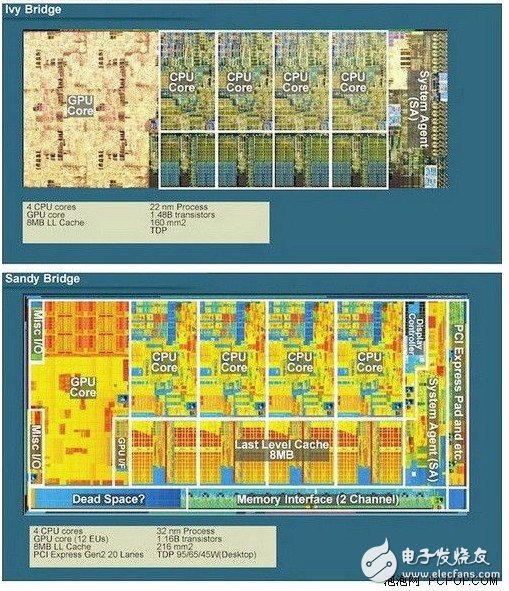
However, the cache capacity is not as large as possible. In addition to the high cost of SRAM, the area limitation of the CPU chip is also one of the important factors. As the CPU integrates more and more computing units, the number of transistors in each generation of processors has increased significantly compared to the previous generation. However, as the manufacturing process has repeatedly encountered bottlenecks, Moore's Law has frequently been questioned. Fortunately, 3D Tri-Gate technology Temporarily alleviating this problem, the latest Ivy Bridge has 28% more transistors than Sandy Bridge when the cache capacity remains unchanged. The extra transistors are mainly used to enhance the performance of the nuclear display. Then the current Ivy Bridge has 28% more transistors than Sandy Bridge. Is 8MB L3 cache sufficient for these processors?
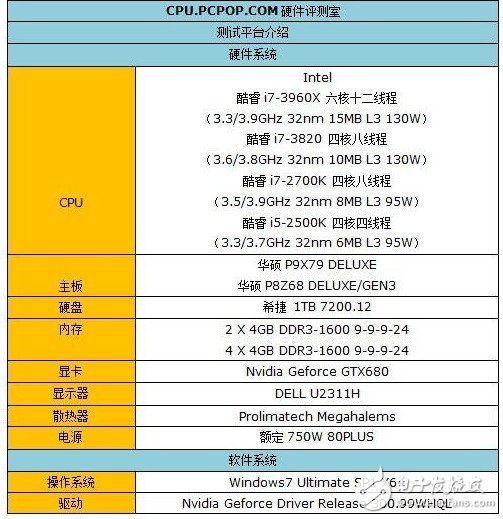
In this test, we used Intel Core i5-2500K, Core i7-2700, Core i7-3820 and flagship Core i7-3960X for testing. The supporting motherboards are ASUS P8Z68 DELUXE/GEN3 and ASUS P9X79 DELUXE.
In the test, we locked the main frequency of the processor at 3.0GHz, 4.0GHz (Turn off HT Hyper-Threading), and 4.0GHz (Turn on Hyper-Threading) to eliminate the interference of other factors. The test items selected Super PI, wPrime, WinRAR, Fritz Chess Benchmark, Cinebench R11.5 and 3DMark 11.
Super PI is a software dedicated to testing the stability of the CPU. The software allows the CPU to operate under high load by calculating the pi ratio, so as to test the CPU's computing power and stability.
â— 3.0GHz frequency

â— 4.0GHz frequency
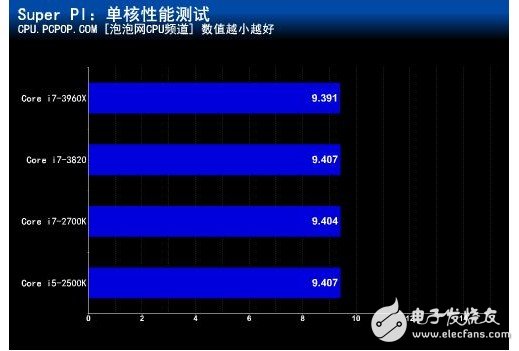
In the single-core performance test, the three-level cache capacity did not cause much change.
wPrime is a common multi-threaded computing test tool, which is more accurate than Super Pi when testing the performance of multi-core processors. Unlike SuperPI's single-threaded operation, wPrime can support multiple core processor operations, even 8-core processors, when opening a software interface.
â— 3.0GHz frequency
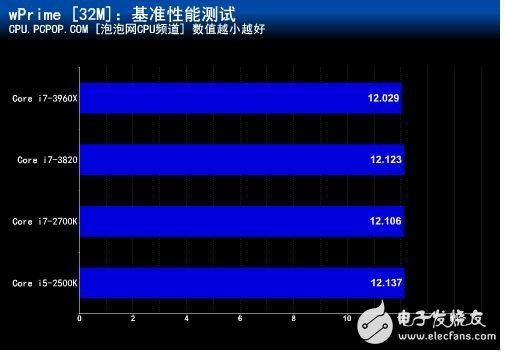
â— 4.0GHz frequency
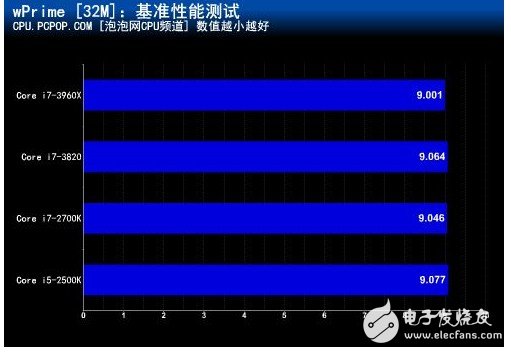
â— Enable Hyper-Threading at 4.0GHz main frequency
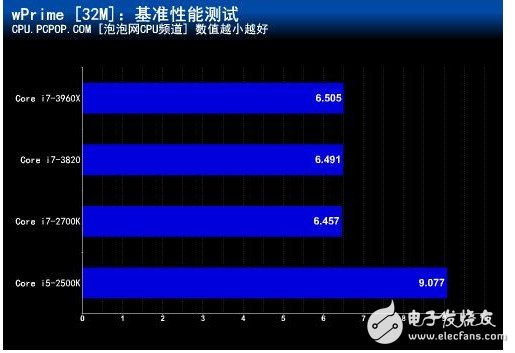
In the wPrime multi-threaded performance test, the difference in the three-level cache capacity did not cause any impact.
The first test item is the latest 3D performance benchmarking software 3DMark 11, which is Futuremark's latest DX11 graphics performance test tool. It also takes into account the ability of the CPU processor to cooperate, especially in parallel computing. 3DMark 11 is based on the native DX11 engine and fully uses all the new features of the DX11 API, including tessellation, computing shaders, and multithreading. 3DMark 11 inherits and improves the statistical method of 3DMark Vantage, removing the high-end (H) that hardly anyone uses.
Judging from the test results, at low clock speeds, the L3 cache capacity has minimal impact on CPU performance. After overclocking to 4GHz and the same number of cores, the CPU with 15MB L3 cache is only 4% higher than the 6MB score. One situation remains the same after the Hyper-Threading technology is turned on. The 15MB L3 Core i7-3960X is only 4% higher than the 8MB Core i7-2700K (Because the Core i5-2500K does not support Hyper-Threading, the data here is not For comparison, the same below).
CineBench uses the Cinema 4D special effects software engine developed for the film and television industry to test the performance of the CPU and graphics card. The latest version R11.5 has further strengthened the computing power. Even the most powerful processors at present are difficult to be tested in this test. Get high scores.
Test results show that in the scientific computing test, the difference in L3 cache capacity did not cause much difference.
WinRAR is a file compression management sharing software that uses a lot of users. It provides highly optimized optional compression algorithms for multimedia data, and can support processor multi-threading.
â— 3.0GHz frequency
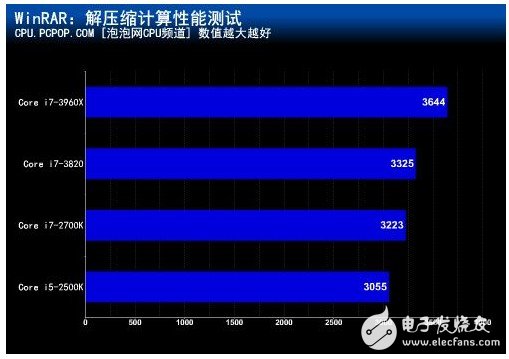
â— 4.0GHz frequency
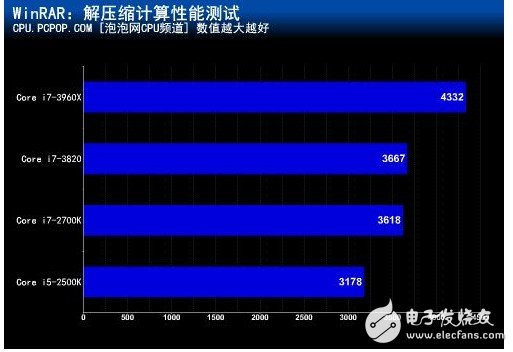
At low frequencies, the difference in L3 cache capacity causes a maximum performance difference of 19%. When the main frequency exceeds 4GHz, the Core i7-3960X with 15MB L3 cache is 36% higher than the Core i5-2500K with 6MB. . â— Enable Hyper-Threading at 4.0GHz main frequency
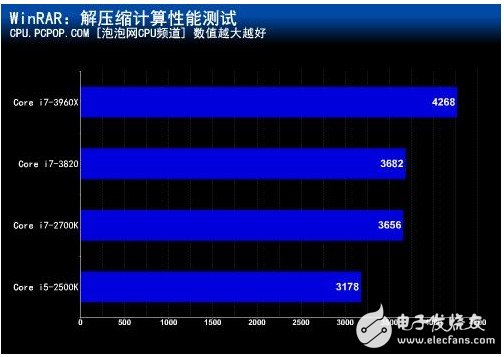
â— Summary
From this test, the difference in the capacity of the three-level cache did not cause much change in performance. The average increase of 15MB of the third-level cache compared with 6MB was less than 4%, which only caused 19 in the WinRAR decompression performance test with high data calculation. % Difference. In contrast, the CPU performance gap before and after overclocking is more obvious. In the test for multi-threading optimization, the CPU performance gap after turning off the hyper-threading technology is also more obvious, so the current improvement of CPU performance The best way is to increase the CPU frequency, and for the three-level cache, Intel obviously has its own plans. â–
ConclusionThis is the end of the introduction to the CPU cache. I hope this article will give you a more comprehensive understanding of the CPU cache. If you have any deficiencies, please correct me.
Braided Sleeve,Braided Cable Sleeve,Expandable Braided Sleeving,Braided Wire Sleeve
Shenzhen Huiyunhai Tech.Co., Ltd. , https://www.cablesleevefactory.com