introduction
GPS is a terminal for positioning or navigation by receiving satellite signals. The antenna must be used to receive the signal. The GPS satellite positioning solution is a process of calculating information such as the position P, speed V, and time T of the receiver based on measured values ​​such as pseudorange and pseudorange increment. At present, the two most commonly used methods in GPS real-time positioning solution are iterative least squares algorithm (ILS) and extended Kalman filter (EKF). In order to accurately calculate the three-dimensional position of the receiver and the value of the time unknown, the solution process requires measurement information from at least 4 satellites. However, when the GPS signal is blocked, the receiver can only receive the measurement information of 3 satellites, and there are not enough 4 solving equations, and ILS is no longer applicable. Introducing EKF, using multiple sets of data over time to perform real-time positioning calculation, but positioning accuracy is also difficult to meet user needs.
In order to solve the above problems, this paper proposes an improved EKF algorithm. Using the motion characteristics of slow position change in the vertical ground direction, a system model of improved EKF algorithm was established, and the filter parameters were obtained through theoretical analysis, and finally verified with real satellite data. It should be particularly pointed out that, because the improved EKF algorithm proposed in this paper uses the feature of slowly changing position in the vertical ground direction, the applicable occasion of this algorithm is the positioning solution of ground users such as vehicles, and is not suitable for vertical ground High-speed movement.
1 System model of positioning solution
The system model of satellite positioning solution includes two parts: state model and observation model. Let the vectors yt and xt represent the measured values ​​and system state parameters of the system model, respectively:

1.1 Measurement model
The measurement model of the system describes the relationship between the measured values ​​of the system and the system state parameters. The relationship between the pseudorange and the system state parameters can be expressed as:

1.2 State Model
The system state model describes the time update process of the system state parameters. The expression of the update process is:
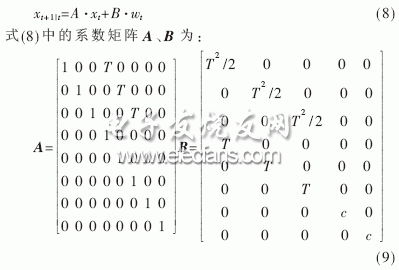
T in equation (9) is the sampling time interval.
The weight in equation (8) represents the noise model of system state transition:

Indoor Fixed Advertising LED Billboard
This series is professionally used for indoor fixed installation of LED display, a variety of installation solutions such as wall installation, simple shelf installation, photo frame installation and so on. Displays advertising video content well indoors. It is suitable for bars, KTV, indoor meeting rooms, exclusive stores, inside shopping malls, indoor stores and so on. Indoor Fixed Advertising LED Billboard,beautiful cabinet design, seamless connection to realize large-screen display advertisement, high-definition smooth video playback function.

Indoor Fixed Advertising Led Billboard,Indoor Led Wall Billboards,Indoor Fixed Led Billboards,Shopping Mall Led Display
Guangzhou Cheng Wen Photoelectric Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ledscreencw.com