The ISDB standard is a digital broadcasting system standard formulated by Japan ’s DIBEG (Digital BroadcasTIng Experts Group). It uses a standardized multiplexing scheme to send various types of signals on a common transmission channel. Multiplexed signals can also be sent out through various transmission channels. ISDB has the characteristics of flexibility, scalability, and commonality, and can flexibly integrate and send multi-program TV and other data services.
The characteristics of the satellite ISDB transmission system have the following main points:
â— MPEG-2 interface: the input signal into the encoder and the output signal from the decoder must comply with the MPEG-2 TS technical specifications;
â— Signal integration based on MPEG-TS: digital content can be reused, and the input code stream does not need to be decoded or re-encoded;
â— The modulation scheme can be chosen flexibly;
â— The specified control signal is used to notify the receiver of multiplexing and decoding and related modulation structure identification.
The general structure of the satellite ISDB general system is shown in Figure 07-05-9.
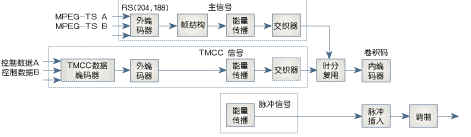
Figure 07-05-9 General structure of the satellite ISDB general system
four. Comparison of several standards
(1) Comparison between DVB and ATSC
The main differences between European "DVB Standard" and American "ATSC Digital TV Standard" are as follows:
(1) Square pixels: "Square Picture Elements" are adopted in the ATSC standard because they are more suitable for computers; and the DVB standard was not initially adopted, and recently adopted. In addition, a wide range of video image formats have also been adopted by DVB, but ATSC does not make this mandatory.
(2) System layer and video coding: Both the DVB and ATSC standards adopt the system layer and video coding of the MPEG-2 standard. However, because the MPEG-2 standard does not specify the video algorithm in detail, the implementation scheme can be different from the two. None of the standards.
(3) Audio coding: DVB standard adopts MPEG-2 audio compression algorithm; ATSC standard adopts AC-3 audio compression algorithm.
(4) Channel coding: The two scramblers (Radomizers) use different polynomials; the two Reed-Solomon forward error correction (FEC) coding uses different redundancy, DVB standard uses 16B, and ATSC standard Use 20B; the interleaving process of the two is different; in the DVB standard Trellix coding has optional different rates, while in the ATSC standard terrestrial broadcasting uses a fixed 2/3 rate grid coding Cable TV does not require grid coding.
(5) Modulation technology: The DVB standard in the satellite broadcasting system uses QPSK, while the ATSC standard does not involve satellite broadcasting. In the cable TV system, the DVB standard uses the optional 16/32 / 64QAM, while the ATSC standard uses 16VSB. The two are completely different. The DVB standard in the terrestrial broadcasting system uses COFDM (2K or 8K carriers) with QPSK, 16QAM or 64QAM; the ATSC standard uses 8VSB.
(2) Comparison of three digital terrestrial broadcasting systems
ISDB-T is very similar to European DVB-T. It can be said that it is a modified European scheme. The transmission scheme is still COFDM. The coding method used is the same and the modulation method is the same. It is also divided into 2K and 8K modes. Because the radio frequency bandwidth of Japanese TV is 6MHz, the number of carriers and the carrier spacing are different. The comparison between ISDB-T, DVB-T and ATV is shown in Table 07-05-1.
Table 07-05-1 Comparison of three digital terrestrial broadcasting systems
Japan ISDB-T | European DVB-T | American ATSC ATV | |
bandwidth | 5.6MHz, 432kHz | 6.6,7.6MHz | 5.6MHz |
modulation | COFDM | COFDM | 8VSB |
Carrier frequency modulation | DQPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM | QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM | 8VSB |
Carrier frequency | 5.6MHz: 1045 lines (2K mode) 5617 lines (8K mode) | 1705 lines (2K mode) | Single carrier frequency |
Error correction | Convolution (1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8) + RS (204,188) | 2/3 grid code + RS (207,187) | |
Multiplexing | MPEG-2 system | MPEG-2 system | MPEG-2 system |
coding | MPEG-2 encoding | MPEG-2 encoding | MPEG-2 encoding (sound is AC-3) |
Information rate | 5.6MHz: 3.68Mb / s ~ 21.46Mb / s 432kHz: 283kb / s ~ 1.65Mb / s | 4.35Mb / s ~ 31.67Mb / s | 19.39Mb / s |
Mobile reception | can | Difficult (conditional) | Can't |
Simultaneously transmit multiple levels of images (HDTV, SDTV, LDTV), transmit multiple sets of programs, and simultaneously perform image, voice, and data services. These are the common advantages of digital TV, and are applicable to the three standards of the United States, Europe, and Japan. The strong anti-multipath capability, which can be layered, mobile reception, and can form a single frequency network are the advantages of OFDM, and the common advantages of European and Japanese standards. According to the hierarchical and narrowband reception, the fixed reception, mobile reception and portable reception are realized at the same time, which is only a characteristic of the Japanese system. Compared with DVB-T, ISDB-T adds some receiving and layered transmission functions.
The so-called partial reception means that the system divides the entire 6MHz bandwidth into 13 sections, each section of 423kHz, which mainly solves the problem of simultaneous reception of narrowband and broadband services. Its receiver can receive the 6MHz full bandwidth, and can also receive the narrowband 423kHz at the center of the band signal. The former is mainly used for fixed and mobile mobile reception, while the latter is mainly used for small portable receivers, but due to the narrow bandwidth and poor reception conditions, it can only be used for audio broadcasting and data. In this way, it may not be necessary to have a separate digital broadcast (DVB). But this raises new questions about the operation of radio and television stations.
The so-called layering refers to different settings for different segments of error correction and modulation methods to target different levels of information and different reception conditions and different reception areas. The system is divided into four layers, for example, layer A can have the highest reliability and is used to transmit important information necessary for decoding, while other layers can arrange different protection rates to adapt to different services.
Fives. Digital TV in my country
In 1995, China established the first HDTV coordination group, and its members were composed of the heads of ministries and commissions such as the Ministry of Radio, Film and Television, and the Ministry of Electronics. In the second half of 1995, China Central Television introduced the SDTV grade digital TV equipment of the United States General Instruments (GI) Company, and began the satellite transmission of all digital TV signals. In August 1996, CCTV launched the satellite digital TV (SDTV) broadcasting service, which was at the forefront of Asian countries. In January 1997, 11 television programs in 10 provinces and districts including Guangdong and Henan have been transmitted via satellite using the all-digital method of MPEG-2 compression technology. In 1998, another six provinces and cities also used digital transmission of satellite programs. And on October 1, 1999, CCTV conducted a pilot broadcast of the 50th National Day parade using the digital TV terrestrial broadcasting method.
In April 1999, China established the National Digital TV Research and Development and Industrialization Leading Group to unify the development of digital TV. In June 2000, the State Planning Commission determined that Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen would start the research, development and application of digital TV, thus kicking off the development of China's digital TV industry.
From 2000 to 2001 was the digital TV pilot year. Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen conduct digital TV trials.
As of May 2001, all provincial and municipal TV stations in China have adopted satellite transmission channels and have opened satellite digital TV channels.
The digital TV industrialization project has been included in the 12th National High-tech Project in the National Tenth Five-Year Plan. And plan:
2002 China's digital TV standard formulation
2003 Commercial Digital TV Broadcast Trial
In 2005, a quarter of the national television stations launched and transmitted digital television signals
In 2010, fully realize digital TV broadcasting
In 2015, the broadcast of analog TV broadcasts was stopped
For digital satellite broadcasting, the US Direc TV uses the DSS format, and most of the satellite platforms later use DVB-S. There are currently three satellite platforms in China, the earliest is the CCTV5, 6, 7, and 8 encryption platforms. Later, the star programs and the village and village platforms in all provinces are digital. China has a corresponding standard, that is, a modified DVB -S. In terms of cable, the downlink broadcasting standard has been basically determined, DVB-C, but the standard for interactive services has not yet been determined.
A GFCI outlet receptacle is different from conventional receptacles.
In the event of a groud fault, a GFCI will trip and quickly stop the flow of electricity to prevent serious injury.
How does LED Trip indicators work?
Indicator: 2 LED Trip Indicators (Red & Green)
• Red-The device needs attention. the device is engineered to conduct a self-test internally every 2 minutes to ensure the protection is on. If the device fails the test, the red light is on to signal that the device should be replaced
• Green-The device has passed self-test and working properly
Regular GFCI UL,Receptacle GFCI,GFCI Outlet with UL943,GFCI Receptacle
Hoojet Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd , https://www.hoojetgfci.com