LED test standard
Semiconductor light-emitting diode (LED) is a new type of luminous body with high electro-optical efficiency, small size, long life, low voltage, energy saving and environmental protection. LED photoelectric test is an important and only means to verify the photoelectric performance of LED. The corresponding test results are the basis for evaluating and reflecting the current development level of China's LED industry. The development of standards for LED photoelectric test methods is an important way to uniformly measure the photoelectric performance of LED products, and it is the premise for the test results to truly reflect the development level of China's LED industry. This article introduces the main aspects of LED's photoelectric performance testing in conjunction with the latest national standards for LED test methods.
Keywords: National standards for semiconductor light-emitting diode test methods
I. Introduction
Semiconductor light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have been widely used in indicator lights, signal lights, instrument displays, mobile phone backlights, car light sources, etc. Especially for the development of white LED technology, LEDs are also more and more widely used in the field of lighting. However, in the past, there were no comprehensive national and industry standards for LED testing. In production practice, only relative parameters can be used as the basis. Different manufacturers, users, and research institutions have been controversial about this, leading to serious development of the domestic LED industry. influences. Therefore, national standards for semiconductor light-emitting diode test methods came into being.
2. LED test method
Based on the actual needs of various LED application fields, LED testing needs to include many aspects, including: electrical characteristics, optical characteristics, switching characteristics, color characteristics, thermal characteristics, reliability and so on.
1. Electrical characteristics
LED is a unipolar PN junction diode made of semiconductor inorganic materials. It is a kind of semiconductor PN junction diode. Its voltage-current relationship is called volt-ampere characteristic. As can be seen from Figure 1, LED electrical characteristics parameters include forward current, forward voltage, reverse current and reverse voltage, LED must be driven by a suitable current and voltage to work properly. The maximum allowable forward voltage, forward current, and reverse voltage and current of the LED can be obtained by testing the electrical characteristics of the LED. In addition, the optimal working electric power of the LED can also be determined. 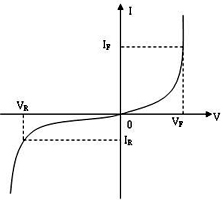
Figure 1 LED volt-ampere characteristic curve
The test of LED electrical characteristics is generally carried out using a voltage and ammeter under the supply of a corresponding constant current and constant voltage source.
2. Optical characteristics
Similar to other light sources, the test of LED light characteristics mainly includes luminous flux and luminous efficiency, radiant flux and radiant efficiency, light intensity and light intensity distribution characteristics and spectral parameters.
(1) Luminous flux and luminous efficiency
There are two methods that can be used for luminous flux testing, the integrating sphere method and the variable angle photometer method. The variable angle photometer method is the most accurate method for measuring luminous flux, but due to its longer time-consuming, the sphere method is generally used to test the luminous flux. As shown in Fig. 2, there are two test structures in the existing integrating sphere method for measuring LED luminous flux, one is to place the tested LED at the center of the ball, and the other is to place it on the wall of the ball. h: ^ E8 (d 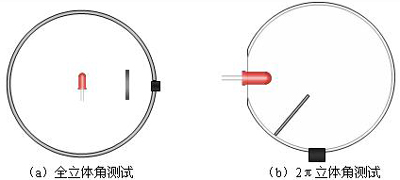
Figure 2 Integrating sphere method to measure LED luminous flux
In addition, because the self-absorption of light by the light source will affect the test results when the sphere method is used to measure the luminous flux, auxiliary lights are often introduced, as shown in Figure 3. 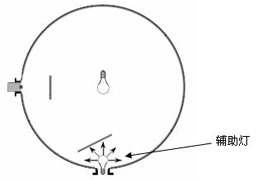
Figure 3 Auxiliary lamp method to eliminate the effect of self-absorption
After the luminous flux is measured, the luminous efficiency of the LED can be measured with an electrical parameter tester. The test methods of radiant flux and radiation efficiency are similar to the test of luminous flux and luminous efficiency.
(2) Light intensity and light intensity distribution characteristics 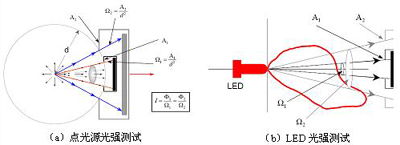
Figure 4 Problems in LED light intensity test
As shown in Figure 4, the light intensity of the point light source is evenly distributed in all directions of the space, and the test results received by detectors with different receiving apertures at different distances will not change, but the inconsistency of the LED light intensity makes the test results It varies with the test distance and detector aperture. Therefore, CIE-127 puts forward two recommended test conditions so that each LED can be tested and evaluated under the same conditions. At present, CIE-127 conditions have been cited by various LED manufacturers and inspection agencies. 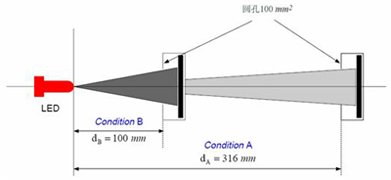
Figure 5 CIE-127 recommended LED light intensity test conditions
(3) Spectral parameters
The spectral characteristic parameters of LED mainly include peak emission wavelength, spectral radiation bandwidth and spectral power distribution. The spectrum of a monochromatic LED is a single peak, and its characteristics are expressed in terms of peak wavelength and bandwidth, while the spectrum of a white LED is composed of multiple monochromatic spectra. The spectral characteristics of all LEDs can be represented by the spectral power distribution, and the chromaticity parameters can also be calculated from the spectral power distribution of the LEDs.
The measurement of the spectral power distribution needs to be carried out by splitting, which distinguishes the various colors of light from the mixed light for measurement. Generally, prisms and gratings can be used for splitting. 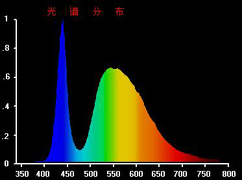
Figure 6 White LED spectral power distribution
3. Switching characteristics
LED switching characteristics refer to the characteristics of light, electricity, and color changes at the moment of LED power-on and power-off. Through the test of the LED switching characteristics, the changing rules of the working state and material properties of the LED at the moment of power on and off can be obtained, which can not only understand the loss of the power on and off to the LED, but also can be used to guide the design of the LED driver module.
4. Color characteristics
The color characteristics of LEDs mainly include chromaticity coordinates, dominant wavelength, color purity, color temperature and color rendering, etc. The color characteristics of LEDs are particularly important for white LEDs.
Existing color characteristic test methods include spectrophotometry and integration methods. As shown in Figure 7: Spectrophotometry is to measure the spectral power distribution of the LED by monochromator spectrometry, and then use the chromatic weighting function to integrate to obtain the corresponding chromaticity parameters; the integration method is to use a specific color filter and a photodetector to directly measure Chromaticity parameter; the accuracy of spectrophotometry is much higher than that of integration method. 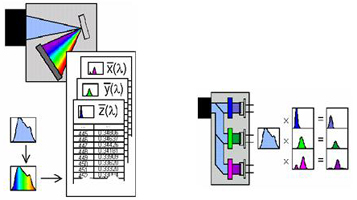
Figure 7 LED color characteristic test method
5. Thermal characteristics
The thermal characteristics of LED mainly refer to thermal resistance and junction temperature. Thermal resistance refers to the ratio of the temperature difference along the heat flow channel to the power dissipated in the channel. The junction temperature refers to the PN junction temperature of the LED. The thermal resistance and junction temperature of the LED are important factors that affect the photoelectric performance of the LED.
Existing tests for LED junction temperature generally have two methods: one is to use an infrared temperature microscope or a miniature thermocouple to measure the surface temperature of the LED chip and regard it as the junction temperature of the LED, but the accuracy is not enough; the other one This is to determine the junction temperature of the LED by using the relationship between the forward bias voltage and the inverse change in junction temperature at the determined current.
6. Reliability
The reliability of LEDs includes electrostatic sensitivity characteristics, lifespan, and environmental characteristics. The electrostatic sensitivity characteristic refers to the electrostatic discharge voltage that the LED can withstand. Some LEDs have higher resistivity and the distance between the positive and negative electrodes is very short. If the electrostatic charge at both ends accumulates to a certain value, this electrostatic voltage will break down the PN junction. Therefore, the electrostatic sensitivity characteristic of the LED must be tested to obtain the critical voltage of the electrostatic discharge failure of the LED. At present, the human body model, the machine model, and the device charging mode are generally used to simulate the electrostatic discharge phenomenon in real life.
In order to observe the change law of the light performance of the LED under long-term continuous use, it is necessary to conduct a sampling test on the LED and obtain the LED life parameters through long-term observation and statistics. For the test of LED environmental characteristics, it is often used to simulate various natural attacks encountered by LEDs in applications. Generally, they include: high and low temperature impact test, humidity cycle test, humidity test, salt spray test, sand and dust test, irradiation test, vibration and vibration. Impact test, drop test, centrifugal acceleration test, etc.
3. The formulation of national standards
Summarizing the above test methods, the National Standards for Test Methods of Semiconductor Light Emitting Diodes have made corresponding regulations on LED electrical characteristics, optical characteristics, thermal characteristics, electrostatic characteristics and life test.
For the electrical characteristics test, the standard specifies the test block diagram of the LED forward voltage, reverse voltage, and reverse current; for the luminous flux test, the standard specifies the 2Ï€ solid angle test structure; for the light intensity test, the standard refers to CIE-127 Recommended conditions; In addition, clear regulations are made on the spectrum test, thermal characteristics test, electrostatic discharge sensitivity test, life test, etc.
4. Conclusion
The formulation of national standards summarizes the existing LED test methods, and upgrades the scientifically applicable methods to standard test methods, which eliminates the differences in the field of LED testing from all walks of life, and makes the test results more truly reflect China ’s LED. The overall level of the industry. However, in view of the continuous development of LED technology, the formulation of national standards is not once and for all, and the latest and most appropriate test technology should always be introduced into the standard.
The Portable Ground Control Statioin with Dual Screend and Dual Operating System Windows/Android, Support 14 CH input/output, HDMI video link for realtime monitoring,Maximus 30km Control Range.
Portable Uav Ground Station,Drone Control Station,Uav Ground Control Station,Drone Ground Control Station,Drone Ground Control System
shenzhen GC Electronics Co.,Ltd. , https://www.jmrdrone.com