The wave of Internet of Things is still surging, and the requirements of Internet of Things applications are increasing. LoRa is a narrow-band wireless technology used to achieve geolocation. LoRa positioning technology is also a feature of multi-scenario applications.
According to research, by the end of 2020, the Internet of Things will have more than 1.5 billion connected devices. About one-third of them will rely heavily on geographic data, and 60% of applications will likely include geographic data. Internet of Things applications are increasingly demanding positioning, especially for asset tracking applications.
The particularity of LoRa is that as long as the endpoint communicates with the network, geographic location data is available, with little impact on the bill of materials and power consumption.
The LoRa-based geographic location can work both outdoors and indoors, with accuracy depending on terrain and base station density.
Principle of LoRa positioningAs a narrowband wireless technology, LoRa uses geostation time difference to achieve geolocation.
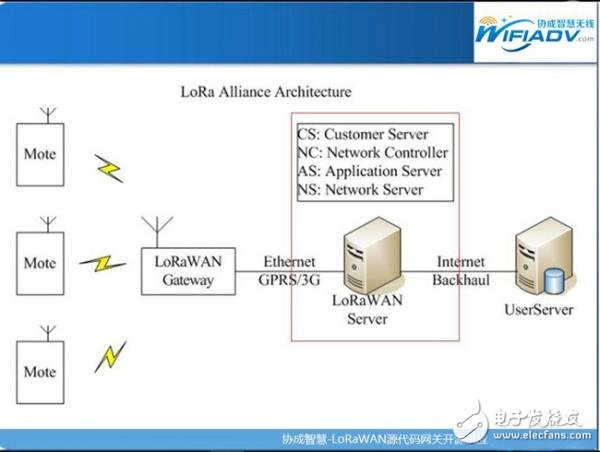
To understand how LoRa positioning works, take a look at the data transfer steps from the endpoint to the server. The premise of LoRa positioning is that all base stations or gateways share a common time base.
When any LoRaWAN terminal device sends a packet, it is received by all gateways within its network, and each message is reported to the network server. All gateways are the same, they always receive signals at all data rates on all channels.
This means there is no overhead on the LoRa end devices because they do not need to be scanned and connected to a particular gateway. The sensor is simply woken up, sending packets, and all gateways within the network can receive it.

Lowest power consumption
There is no processing of location tasks in the sensor; no "air time" is required to send location data; geolocation can be located using LoRaWAN packets as small as possible.
Lowest cost
There are no GNSS or other hardware in the sensor; smaller batteries, because the sensor power is not used to get the position; the smallest size, including the electronic part, the battery, the case.
Minimum environmental impact
Sensor hardware is minimized (including electronics, battery, case size, etc.); many sensors have a lifetime battery installed.
LoRa positioning application scenario 1. Smart city and traffic monitoringGeolocation features in automotive applications can be used for incident tracking and notification, as well as predictive maintenance needs. The specific location data helps the algorithm make better predictions.
2. Measurement and logisticsThe positioning function has various applications in logistics. Includes fill rate monitoring for trash cans, recycling bins, gas canisters, or any other container.
Data can be used to automatically optimize collection routes and save operating costs. In addition, geolocation can be used for asset tracking for more efficient inventory management.
3. AgricultureLoRa positioning is currently used for livestock tracking. By tracking cattle and monitoring their health, for example, you can take care of sick cows faster and easier. On a large ranch, knowing the specific location of the sick animal can significantly increase the reaction time.
LoRa's geographic location is also used in the construction, insurance and consumer industries to track high-value assets such as construction materials, insurance products, pets and even people!
At present, the two major Internet of Things networks in the world, NB-IoT and LoRa, are developing rapidly in China. Relevant departments have counted more than 1,000 Internet of Things applications that have been introduced to various provinces in China. It is reported that 70% of enterprises actively seek mature, reliable and fast-moving IoT products. Most enterprises purchase NB-IoT and LoRa IoT solutions from Fuzhou Xiecheng Wisdom Technology Co., Ltd., including LoRa gateway, smoke, water Dozens of IoT products such as monitoring, infrared detection, positioning, and plugging, and other generations of NB-IoT and LoRa IoT products, in order to quickly develop the Internet of Things business, and become the leader of the Internet of Things across the country. The situation of "World Internet of Things Development Seeing China" is gradually taking shape.
2.5MM Wire To Board Connectors
2.5MM Wire To Board Connectors.
Connectors can be classified into three basic types: line to line, line to board and board to board. These three types of connections are not entirely different. There are two reasons for this type of overlap. First of all, the design of the same connector only needs to be redefined after slightly changing the connection mode, that is to say, it becomes a new design scheme that can be applied to another type of connection mode; secondly, a cable can be installed with a line to line connector at one end and a line to board connector at the other end during assembly, for example, the appearance of class 5 I / O connector is the most common one See for example. If we avoid the fuzziness of this kind of connection, it will provide an effective basis for connector classification.
2.5MM Wire To Board Connectors
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenksocket.com